 Remember this immensely popular guest post from last year? Click on the image for my interview of its hardworking and inspiring author, body-image activist Min-ji Kim. Frankly, it’s well overdue!
Remember this immensely popular guest post from last year? Click on the image for my interview of its hardworking and inspiring author, body-image activist Min-ji Kim. Frankly, it’s well overdue!
Category: Body Image
Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 7: Keeping abreast of Korean bodylines
 Source, edited
Source, edited
Yes, I know. Korean bodylines again. Surely, I really do have some kind of fetishistic obsession with them, as my trolls have long maintained.
Perhaps. Mainly, it’s because I’ve been very busy giving this presentation about them at Korean universities these past two months. Even, I’m very happy to report, getting invited back to some, and finally—squee!—making a small profit too. S-lines, I guess, are now very much my thing.
Instead of feeling top of my game though, frankly I’m wracked by self-doubt. I constantly worry about coming across a real fashion-history expert in the audience, who will quickly reveal me to be the rank amateur I really am.
 Source: Heal Yourself, Skeletor
Source: Heal Yourself, Skeletor
So, to forestall that day for as long as possible, here is the first of many posts this summer correcting mistakes in my presentation I’ve found, and/or adding new things I’ve learned. But first, because it’s actually been over a year since I last wrote on this topic, let me remind you of the gist:
1) Korea’s “alphabetization” (bodylines) craze of the mid-2000s has strong parallels in the rationalization of the corset industry in Western countries in the 1910s to 1940s.
2) Fashion and—supposedly immutable and timeless—beauty ideals for women change rapidly when women suddenly enter the workforce in large numbers, and/or increasingly compete with men. World War Two and the 1970s-80s are examples of both in Western countries; 2002 to today, an example of the latter in Korea.
3) With the exception of World War Two though, when the reasons for the changes were explicit, correlation doesn’t imply causation. Noting that bodylines happened to appear during a time of rapid economic change in Korea does not explain why they came about.
Maybe, simply because there’s nothing more to explain, and we should be wary of assuming some vast patriarchal conspiracy to fill the gap, and/or projecting the arguments of Naomi Wolf’s The Beauty Myth (1990) and Susan Faludi’s Backlash (1991) to Korea. Indeed, arguably it’s mostly increased competition since the Asian Financial Crisis that has profoundly affected the demands on job-seekers’ appearances, of both sexes. Also, the financial demands of the K-pop industry go a long way towards explaining the increased sexual objectification in the media in the past decade.
Which brings me to today’s look at the evolving meaning of “glamour” in American English, which I use to illustrate the speed of those changes in World War Two:
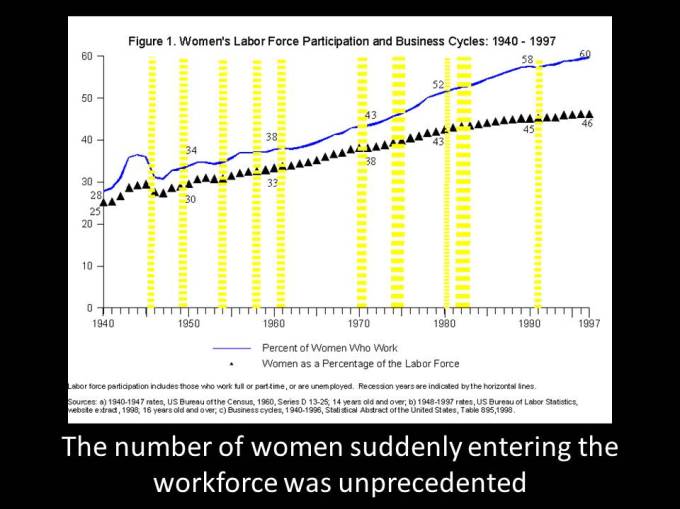






 These are necessary generalizations of course, whereas the reality was that contradictory and competing trends coexisted simultaneously, which you can read about in much greater depth back in Part 4. But this next slide was just plain wrong:
These are necessary generalizations of course, whereas the reality was that contradictory and competing trends coexisted simultaneously, which you can read about in much greater depth back in Part 4. But this next slide was just plain wrong: With that slide, I went on to give a few more examples to demonstrate how glamour, then meaning large breasts, soon came to mean just about anything. But then I read Glamour: Women, History, Feminism by Carol Dyhouse (2010), and discovered that the word has always been very vague and malleable (albeit still always meaning bewitching and alluring). Moreover, to my surprise, “breasts”—the first thing I look for in new books these days—weren’t even mentioned in the index. Nor for that matter, “glamour” in Breasts: A Natural and Unnatural History by Florence Williams (2013) either. Given everything I’ve said and written about them, I feel they deserved more attention that that (although Dyhouse does cover them in the chapter “Princesses, Tarts, and Cheesecake” somewhat), but certainly there was only ever a strong association with glamour at best. Also, my timing was wrong, for that association began as early as the late-1920s, and didn’t peak until after the war. (See the introduction or from page 134 of the dissertation Hollywood Glamour: Sex, Power, and Photography, 1925–1939, by Liz Willis-Tropea, 2008.)
With that slide, I went on to give a few more examples to demonstrate how glamour, then meaning large breasts, soon came to mean just about anything. But then I read Glamour: Women, History, Feminism by Carol Dyhouse (2010), and discovered that the word has always been very vague and malleable (albeit still always meaning bewitching and alluring). Moreover, to my surprise, “breasts”—the first thing I look for in new books these days—weren’t even mentioned in the index. Nor for that matter, “glamour” in Breasts: A Natural and Unnatural History by Florence Williams (2013) either. Given everything I’ve said and written about them, I feel they deserved more attention that that (although Dyhouse does cover them in the chapter “Princesses, Tarts, and Cheesecake” somewhat), but certainly there was only ever a strong association with glamour at best. Also, my timing was wrong, for that association began as early as the late-1920s, and didn’t peak until after the war. (See the introduction or from page 134 of the dissertation Hollywood Glamour: Sex, Power, and Photography, 1925–1939, by Liz Willis-Tropea, 2008.)
For instance, take this excerpt from Uplift: The Bra in America by Jane Farrell-Beck and Colleen Gau (2002, page 103; my emphasis):
The War Production Board severely restricted the use of chromium-plated wire for civilian-use products. Brassiere manufacturers improved fasteners, but renounced wiring. Besides, glamour was not what brassieres were about in 1941-45. Posture, health, fitness, and readiness for action constituted the only acceptable raisons d’être for undergarments-at-war, dubbed “Dutiful Brassieres” by the H & W Company.
Indeed, it turns out those lingerie ads in one of my slides come from 1948 and 1949 respectively (and I’ve no idea what that girdle ad was doing there!). And here’s another excerpt, from The Home Front and Beyond: American Women in the 1940s by Susan M. Hartmann (1983, page 198; my emphasis):
Women adapted their appearance to the wartime look, which deemphasized physical differences between the sexes, but they did not completely abandon adornments symbolizing femininity. While some adjusted to the disappearance of silk and nylon by going barelegged, others used leg makeup and some even painted on a seam line. Women emphasized their lips by favoring dark colors. The focus on breasts did not peak until later, but the sweatergirl look, popularized by Lana Turner and other movie stars, had its origins in the war years, and women competed in Sweater Girl contests as early as 1943.
In short, the trend is still there, and, “much of women’s social history [being] embedded in clothes, cosmetics, and material culture” (Dyhouse, p. 7.), remains fascinating for how, as a product of the era when cinema first began to have a profound impact on fashion, it set the standard of slim waists and large breasts that largely remains in Western—and global—culture today.
But covering all that in a stand-alone presentation, which I’ve really struggled to get down to an hour a half? In hindsight, it’s a poor, unnecessarily complicated choice to get my point about rapid change across.
 Source: How do ya like me now?
Source: How do ya like me now?
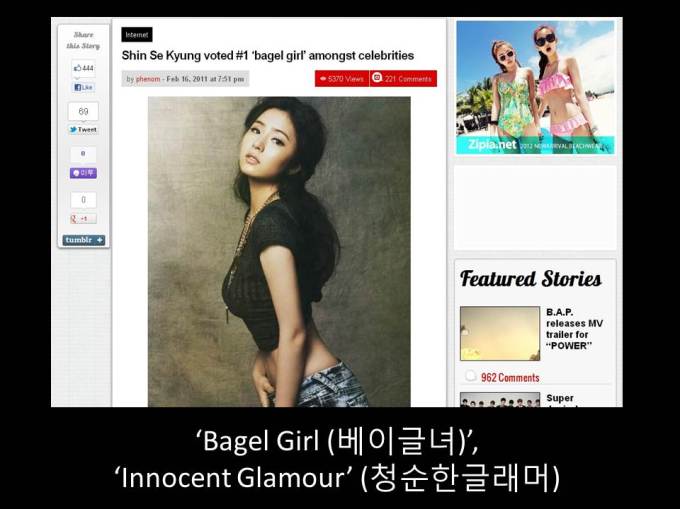
Likely, I fixated on glamour because it’s where “Bagel Girl” (베이글녀) derives from, a Korean bodyline that’s been popular for about 4-5 years. A blatantly infantilizing and objectifying term, I was happy to read back in 2011 that Shin Se-kyung at least has rejected being labeled as such (alas, Hyoseong of Secret is quite happy with it), echoing Lana Turner’s distaste at being the first “Sweater Girl.”
Then I discovered the Bagel Girl had a precedent in the “Lolita Egg” (롤리타 에그) of 2003, which, as the following advertorial explains, likewise emphasized the childish features of female celebrities then in their early-20s—who would surely have preferred being better known as adults instead. While I genuinely despair that its authors and interviewees actually got paid for their work (you’ll soon see why!), it does demonstrate the remarkable historical continuity to medical discourses about “Western” and “Asian” women’s bodies, and of the incessant drive to infantilize their owners.
 ‘롤리타-에그’ 얼굴 뜬다…2000년대 미인은 ‘어린소녀+계란형’ The “Lolita Egg” Face …Beauties of the 2000s have ‘Young girl + Egg Shape’
‘롤리타-에그’ 얼굴 뜬다…2000년대 미인은 ‘어린소녀+계란형’ The “Lolita Egg” Face …Beauties of the 2000s have ‘Young girl + Egg Shape’
Donga Ilbo (via Naver), November 2, 2003
이승재기자 sjda@donga.com, 조경복기자 kathycho@donga.com / By Lee Sung-jae and Jo Gyeong-bok
‘롤리타-에그 (Lolita-Egg)’형 얼굴이 최근 뜨고 있다 The ‘Lolita Egg’ Face Trend Has Been Booming Recently
1990년대 성숙한 미인상으로 각광받던 ‘계란(Egg)’형 얼굴의 연장선상에 있으면서도, 길이가 짧은 콧등과 좁은 턱, 넓은 이마 등 어린 아이의 이미지로 ‘롤리타 콤플렉스’(어린 소녀에 대한 성적 충동·롤리타는 12세 소녀를 향한 중년 남자의 광적인 사랑을 담은 블라디미르 나보코프의 동명 소설에 등장하는 소녀 이름)를 자극하는 ‘이중적 얼굴’이 주목받고 있는 것.
While the 1990s trend for mature, beautiful women with egg-like faces continues, now it has combined with a short nose-bridge, narrow chin, and wide forehead, reminiscent of a child’s. This ‘double face’ stimulates the ‘Lolita Complex’, based on the Lolita novel by Vladimir Nabokov (1955), about a middle-aged man’s insane love and sexual urges for a 12 year-old girl of the same name.
 Source
Source
‘롤리타-에그’형의 대표는 탤런트 송혜교(21)와 가수 이효리(24)다. 또 드라마 ‘선녀와 사기꾼’(SBS), ‘노란손수건’(KBS1)에 이어 SBS ‘때려’에 출연 중인 탤런트 소이현(19)과 영화 ‘최후에 만찬’에 비행(非行) 소녀 ‘재림’으로 나오는 신인 조윤희(21)도 닮은꼴이다.
Representative stars with the Lolita Egg face shape are talent Song Hye-Kyo (21; Western ages are given) and singer Lee Hyori (24). Other women that resemble them include: the drama talent So Yi-hyun (19), who has appeared in Fairy and Swindler (SBS), Yellow Handkerchief (KBS1), and is currently starring in Punch (SBS); and movie rookie Jo Yoon-hee (21), who played the character Jae-rim in The Last Supper (2003).
조용진 한서대 부설 얼굴연구소 소장은 “이 얼굴형은 자기중심적이면서도 콧대가 높지 않아 ‘만만한’ 여성상”이라며 “경제 불황이 장기화하면서 퇴폐적이면서 유아적인 여성상을 찾는 동시에 수렁에서 구원해 줄 강력하고 성숙한 여성상을 갈구하고 있다는 표시”라고 분석했다.
Jo Yong-jin, head of the Face Research Institute affiliated with Hanseo University, explained “While this face shape is self-centered, the nose bridge is not high, making it a manageable female symbol,” and that “While the recession prolongs, people long for a decadent but childlike female symbol, but at the same time also strongly long for a mature female symbol to save them from the depths.”
롤리타 에그’ 얼굴의 특징 Unique Points about the Lolita Egg Face
얼굴선은 갸름하지만 전체적으론 둥그스름하고 부드럽다. ‘롤리타 에그’형은 90년대 채시라와 최진실에서 보듯 갸름한 듯하면서도 약간 네모진 미인형에 비해 특징이 적다. ‘어디선가 본 듯한’ 느낌을 주어 대중성이 강하다.
The face-line is slender, but overall it is roundish and soft. As you can see from images of Chae Shi-ra and Choi Jin-sil, in the 1990s the Lolita Egg face shape  also looked slender, but compared to slightly square-faced beauties didn’t have many characteristics. It was massively popular, because it gave the feeling of a face you could see anywhere (source, right).
also looked slender, but compared to slightly square-faced beauties didn’t have many characteristics. It was massively popular, because it gave the feeling of a face you could see anywhere (source, right).
얼굴의 포인트는 코. 채시라 등의 코는 높으면서도 콧등이 긴데 반해 이 얼굴형은 콧등이 낮고 그 길이가 짧아 ‘콧대가 높다’는 느낌이 없다. 다만 코끝이 버선코 모양으로 솟아올라 비순각(鼻脣角·코끝과 인중 사이의 벌어진 정도·그림)이 90도 이상인 것이 특징. 코가 짧은 동양적 특징과 비순각이 큰 서양적 특징(한국인은 평균 90도가 채 못 되나 최근 120도까지 끌어올리는 성형수술이 유행이다)이 동시에 나타난다.
The point of the face is the nose. Compared with the cases of Chae Shi-ra and so on, whose noses are high and have long nose bridges, the nose bridge of a Lolita Egg face is low and short, so it doesn’t give the feeling of a high nose bridge. However, the tip of the Lolita Egg nose is marked for resembling the tip of a bi-son (a traditional women’s sock), soaring upward, and the philtrum is more than 90 degrees (see picture). A Lolita Egg face has a combination of this philtrum, which is a Western trait (Koreans typically have one less than 90 degrees; however, the trend in cosmetic surgery is to get one between 90 and 120 degrees) and a short nose, which is an Asian trait.
미고 성형외과 이강원 원장은 “다소 나이 들어 보이고 노동을 즐기지 않는 듯한 느낌을 주는 긴 코에 비해 짧고 오뚝한 코는 귀엽고 애교 있으며 아이 같은 이미지를 준다”고 말했다. 이런 코는 이미연의 두텁고 귀티 나는 코가 주는 ‘접근하기 어려운’ 느낌에 비해 ‘만인이 사랑할 수 있을 것 같은’ 느낌을 유발한다.
Migo Cosmetic Surgery Clinic head Won Chang-un said “A long nose gives an impression of age and that one doesn’t enjoy one’s work, whereas a short but high nose gives one of cuteness and aegyo. A thick but elegant nose like that of Lee Mi-yeon’s [James—below] gives a cold, stand-offish impression, but a Lolita Egg one gives off one that the woman can be loved by all.
 Source
Source
턱은 앞으로 다소 돌출했지만 턱의 각도가 좁아 뾰족한 느낌도 든다. 이는 일본 여성의 얼굴에 많이 나타나는 특징. 28∼32개의 치아를 모두 담기엔 턱이 좁아 덧니가 있는 경우가 많다. 어금니가 상대적으로 약해 딱딱한 음식을 씹는 것에는 약한 편.
[However], while the jaw of the Lolita Egg protrudes forward, it is narrow, giving a pointy feeling. This is characteristic of many Japanese women [James—see #3 here]. But because 28-32 teeth are crammed into such narrow jaws, there are also many cases of snaggleteeth. The molars also tend to be weak, making it difficult to chew hard food.
눈과 눈썹은 끝이 살짝 치켜 올라가 90년 대 미인상과 유사하나, 눈의 모양은 다르다. 90년대 미인은 눈이 크면서도 가느다란 데 반해 이 얼굴형은 눈이 크고 동그래 눈동자가 완전 노출되는 것이 특징. 가느다란 눈에 비해 개방적이고 ‘성(性)을 알 것 같은’ 느낌을 준다.
The end of the eyes and eyebrows raise up slightly at the ends, resembling the style of 1990s beauties, but the shape is different. Compared to that large but slender style, the Lolita Egg eyes are rounder and more exposed. This gives a feeling of openness and greater sexual experience.
얼굴에 담긴 메시지 The Message in a Face
‘롤리타 에그’형의 여성들은 남성들의 ‘소유욕’을 자극하는 한편 여성들에게 ‘똑같이 되고 싶다’는 워너비(wannabe) 욕망을 갖게 한다. 예쁘면서도 도도한 인상을 주지 않아 많은 남성들이 따른다. 이로 인해 이런 여성들은 선택의 여지가 많아 독점적으로 상대를 고르는 듯한 인상을 주기도 한다.
 On the one hand, the Lolita Egg stimulates men’s possessiveness, whereas to women it turns them into wannabees. It’s a pretty face shape, but doesn’t give off a haughty, arrogant impression, proving very popular with men. Women who have it can pick and choose from among their many male followers (source right: unknown).
On the one hand, the Lolita Egg stimulates men’s possessiveness, whereas to women it turns them into wannabees. It’s a pretty face shape, but doesn’t give off a haughty, arrogant impression, proving very popular with men. Women who have it can pick and choose from among their many male followers (source right: unknown).
인상전문가 주선희씨는 “낮은 코는 타협의 이미지를 주는 데 반해 선명한 입술 라인은 맺고 끊음이 분명한 이미지가 읽힌다”며 “이런 얼굴은 남성을 소유한 뒤 가차 없이 버릴 것 같은 느낌을 주기 때문에 여성들이 강한 대리만족을 얻게 된다”고 말했다.
Face-expression specialist Ju Seon-hee said “A low nose gives an impression that the owner will readily give-in and compromise, whereas the clear lipline of a Lolita Egg gives an image of decisiveness,” and that women with the latter can gain a strong sense of vicarious satisfaction through using (lit. possessing) and then discarding men.”
최근 인기 절정의 댄스곡인 이효리의 ‘10 Minutes’ 가사(나이트클럽에서 화장실에 간 여자 친구를 기다리는 남자를 유혹하는 내용)에서도 나타나듯 “겁먹지는 마. 너도 날 원해. 10분이면 돼”하고 욕망을 노골적으로 강력하게 드러내는 이미지라는 것이다.
Like the lyrics of Lee Hyori’s song 10 minutes say (about a woman who seduces a man at a nightclub while he is waiting for his girlfriend in the bathroom), currently at the height of its popularity, “Don’t be scared. You want me too. 10 minutes is all we need”, this a strong and nakedly desiring image. (End)
 Source
Source
For more on the negative connotations of “Asian” bodily traits, perpetuated by cosmetic surgeons and the media, please see here (and don’t forget Lee Hyori’s Asian bottom!). As for the infantilization of women, let finish this post by passing on some observations by Dyhouse, from page 114 (source, right; emphasis):
Nabokov’s Lolita was published (in Paris) in 1955: the book caused great controversy and was banned in the USA and the UK until 1958. Baby Doll, the equally contentious film with a screenplay by Tennessee Williams, starring Carroll Baker in the role of its lubriciously regressive, thumbsucking heroine, appeared in 1956. The sexualisation of young girls in the  culture of the 1950s had complex roots, but was probably at least in part a male reaction to stereotypes of idealized, adult femininity. Little girls were less scary than adult women, especially when the latter looked like the elegant Barbara Goalen and wielded sharp-pointed parasols. Images of ‘baby dolls’ in short, flimsy nightdresses infantilized and grossly objectified women: they segued into the image of the 1960s ‘dolly bird’, undercutting any assertiveness associated with women’s role in the ‘youthquake’ of the decade.
culture of the 1950s had complex roots, but was probably at least in part a male reaction to stereotypes of idealized, adult femininity. Little girls were less scary than adult women, especially when the latter looked like the elegant Barbara Goalen and wielded sharp-pointed parasols. Images of ‘baby dolls’ in short, flimsy nightdresses infantilized and grossly objectified women: they segued into the image of the 1960s ‘dolly bird’, undercutting any assertiveness associated with women’s role in the ‘youthquake’ of the decade.
Did I say you shouldn’t project Western narratives onto Korea? I take that back. Because goddamn, would that explain a lot of things here!
Update: See here for a Prezi presentation on “Trends of beautiful faces In Korea.”
The Revealing the Korean Body Politic Series:
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic Part 12: If You Don’t Have Kim Yuna’s Vital Statistics, Your Body Sucks and You Will Totally Die Alone
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 11: 노출이 강간 유혹?…허튼소리 말라 Wearing Revealing Clothes Leads to Rape? Don’t Be Absurd
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 10: “An epic battle between feminism and deep-seated misogyny is underway in South Korea”
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 9: To Understand Modern Korean Misogyny, Look to the Modern Girls of the 1930s
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 8: The Bare-leg Bars of 1942
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 7: Keeping abreast of Korean bodylines
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 6: What is the REAL reason for the backlash?
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 5: Links
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 4: Girls are different from boys
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 3: Historical precedents for Korea’s modern beauty myth
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 2: Kwak Hyun-hwa (곽현화), Pin-up Grrrls, and The Banality of Sex and Nudity in the Media
- Bikinis, Breasts, and Backlash: Revealing the Korean Body Politic in 2012
If you reside in South Korea, you can donate via wire transfer: Turnbull James Edward (Kookmin Bank/국민은행, 563401-01-214324)
The Women’s Issue
 Sorry for the slow posting everyone: I recently had food-poisoning, some editing deadlines and my students’ end of semester exams are looming, and on my days off I’ve been on a mini-whirlwind tour of Korean universities giving presentations about body-image. But I hope to be posting again soon, and, until then, the latest issue of Groove Magazine will easily provide more than enough insights and new information to whet your appetites!
Sorry for the slow posting everyone: I recently had food-poisoning, some editing deadlines and my students’ end of semester exams are looming, and on my days off I’ve been on a mini-whirlwind tour of Korean universities giving presentations about body-image. But I hope to be posting again soon, and, until then, the latest issue of Groove Magazine will easily provide more than enough insights and new information to whet your appetites!
If you can’t get a physical copy, please click on the image above to read it at Issuu (a quick registration is required), or to download a PDF (click on “share” to get the link).
Update: I forgot to mention that I was interviewed for Annie Narae Lee’s article on page 58, but it may not appear online unfortunately. Also, I’m still too busy to listen myself, but Groove’s recent podcast on abortion in Korea sounds useful and interesting.
Quick Hit: Consent is STILL Sexy
 (Source: Heal Yourself, Skeletor)
(Source: Heal Yourself, Skeletor)
I’m just sick of Bora’s boobs.
Okay…no, not really. They’re just a constant reminder of the curse of blogging about sexuality and popular culture. Thanks to them, “Consent is Sexy: SISTAR, slut-shaming, and sexual objectification in the Korean idol system” is literally my most viewed post—but also, per view, probably one of the least actually read.
You’d never think it took a month to research and write, and that I consider it one of my proudest blogging achievements.
Ironically for the frustration that causes now though, it too was born out of the frustration of two weeks of watching interviews of SISTAR members, naively hoping that they would reveal something about the extent to which they consented to—indeed, hopefully played an active role in choosing—the sexualized costumes, choreography, and so on provided by their management company. Instead, I was left with nothing more substantial than learning their favorite flavors of ice-creams, and a firm resolve never to watch any more of the crap that counts as most K-pop entertainment.
But finally, nearly a year later, I’ve just learned of two interviews where girl-group members were able to talk about their jobs like actual human beings.
The first, on the new show The Spokespeople (대변인들), where Rainbow’s Jisook, Stellar’s Gayoung, and Dal Shabet’s Subin, from roughly 8:00 to 26:00 (it’s—grr—unavailable in Korea; click here to overcome that) discussed their recent ‘sexy concepts.’ It’s a still a little frustrating in places, the MCs being “spokespeople” for the “weaker people who can’t speak out” apparently meaning that guests should shut up while the MCs speak for them instead, with poor Subin barely getting a chance to speak at all. But when they did, all three sounded quite genuine:
Next, as Asian Junkie put it:
Ex-TAHITI member Sarah Wolfgang (Hanhee) did an AMA on Reddit recently, where she answered questions on everything from a group member smelling like shit to eating disorders.
And you can read a breakdown of the interview there, including those eating disorders, her complete lack of input into her image, and the debts members are sometimes left with.
Finally, it’s not a recent interview, but The Learned Fangirl just did a review of Nine Muses of Star Empire (2012), which I also covered in last year’s post. While that documovie may sound dated by K-pop standards, it easily remains the most revealing look inside the industry, and I completely agree with the authors’ conclusion:
Interestingly, Billboard‘s Jeff Benjamin had a very different take than us on the documentary, calling it a film that would cause “k-pop haters [to] completely shift their paradigm.” We doubt that — instead it will make a manufactured music form seem manufactured. It’s a warts-and-all look behind the curtain of music industry, and is an unsentimental look at what it takes to create pop star fantasy.
Thoughts?
Related Posts:
When K-pop Gets Under Your Skin…
 (Source)
(Source)
My latest piece for Busan Haps, on the contributions that K-pop has made to cosmetic surgery medical tourism.
I chose the topic because I’d always assumed that K-pop was easily Korea’s #1 cultural export. And, building on from that, that surely most medical tourists to Korea would be coming for cosmetic surgery. After all, what would this blog be without all the posts on dieting and body-image narratives in K-pop songs? On stars’ cosmetic, beauty, and dieting-related endorsements? Or, of course, on the ideals set by their bodies themselves?
I couldn’t have been more wrong.
First, because K-pop only accounted for just five per cent of the revenues from cultural content exports in 2013, as demonstrated in this Arirang news report from January. That worked out to $255 million, out of a total of $5.1 billion.
 (Source)
(Source)
Next, because cosmetic surgery tourists only comprised seven point six percent of medical tourists in 2012. Yes, really.
When I wrote the article, I mistook that for the 2013 percentage, which isn’t available yet. But, assuming it remained the same (although the trend is for rapid growth), that would have resulted in a paltry $7.6 million in revenues in the January to November 2013 period, based on these figures that incorporate revenues lost from Korea’s surprisingly high numbers of outgoing medical tourists (unlike the grossly inflated KTO figures).
No wonder “a renowned business professor” recently dismissed the economic benefits of K-pop.
Frankly, another reason I chose this topic was because I expected I’d quickly prove him wrong. Instead, I soon found myself chagrined, forced to concede that perhaps he had a point.
But the long-term benefits? He’s dead wrong about those. To find out why, please see the article!
Corée du Sud La quête du galbe
 (Source)
(Source)
For French speakers, a Libération article about body image and cosmetic surgery in Korea that I was interviewed for recently. Many thanks to Nouvelles d’Asie for and A G on Twitter for passing it on, and for the above photo.
Unfortunately, it’s one Euro for a month’s access. But you can’t ask for much cheaper than that!
Update: The article is freely available now.
Media and Body Image Workshop, Bar Carmen, Seoul, Sunday 30th, 5-8pm



(Sources: left, center, right)
Yes, it’s back on, and I promise that none of my relatives will be in hospital this time!
Once again, please see Disruptive Voices’ Facebook Event page for more details and RSVPs, or if you’re not on Facebook then please feel free to ask any questions in the comments here, and/or to just turn up to Bar Carmen in Itaewon on the day. (Note that it’s not on the main drag though, but on the other side of the hill: see here or here for maps.)
Those Damned Double Eyelids…
How can a society still have Caucasian beauty ideals if its members explicitly don’t want to look White?
 (Source)
(Source)
Ubiquitous skin-whitening ads. Cosmetic surgery clinics with only Caucasians on their websites. Until a few years ago, almost never seeing a Korean lingerie model.
With parents, hakwon-owners, and recruiters demanding only Caucasian English teachers too, you can hardly be blamed for assuming that the corollary of White privilege is Caucasian beauty ideals. Add the large numbers of Korean women who get surgery for double-eyelids or more prominent nose-bridges, features widely perceived as much more common among Caucasians than Koreans, then who hasn’t once thought that Korean women go under the knife because they want to look White?
Of course, actually talk to Korean cosmetic surgery patients, and most take great offense to that notion. And they would surely know their own motivations—much better than any outsiders or newbies to Korea, who may not realize what intellectual baggage and racial stereotypes they’re bringing with them. Also, light skins have been associated with non-farming elites for millennia; Caucasians may be used on cosmetic surgery websites more in an Occidentalist sense to signify class and lifestyle than specific body features; and Caucasians were really only used in lingerie modelling because moonlighting pornography actors tainted it for Korean models. Even double-eyelids may not be as Caucasian as thought, as it is commonly claimed that possibly as many as 50% of Koreans have them (although in my experience, little to no evidence is ever provided for any figure—even by academics).
 (Source)
(Source)
That said, I think commentators can sometimes come across as a little smug and superior as they point out the mistakes of “expats-turned-anthropologists;” after all, expats are just strangers in a strange land, trying to make sense of the place as best they can. What’s more, they don’t form their opinions in a vacuum, they’re not all simply racist, and I hardly countered all their observations with that last paragraph. So it would be incredibly myopic and defensive to just dismiss their opinions, and/or to pretend that current Korean beauty ideals haven’t been at all influenced by the “the very real presence of white people” in Korea in the last 60 years.
In short, Korean beauty ideals are complicated. And sure: perhaps by all those “expats,” I’m really just talking about myself not so long ago (that’s complicated too). Either way, over the years I’ve been reading about body image in Korea, I’ve often been taken aback by the number of academics who didn’t acknowledge how convoluted the subject is. Some just seemed to take Caucasian body ideals as a given. Why? Were they just being lazy? Were they simply parroting the narratives about Korean cosmetic surgery that dominate the English-language media? Hadn’t they ever—damnit—actually talked to Koreans, who would have vehemently denied wanting to look White?
 (Sources: Left, right)
(Sources: Left, right)
Apologies though, for not taking note of exactly who said what at the time, but then I’m not here to attack any convenient strawmen. Instead, I want to pass on an alternative explanation that I’ve just come across:
• First, that however unfairly and irrationally, because different body features, types, and weights have different positive or negative associations (e.g., fat people are lazy; and, jumping ahead, that flat noses and eyelids without a crease have negative connotations in the US)…
• And next, that because these associations are legitimated—indeed, perpetuated—by the seeming scientific rationality and objectivity of cosmetic surgeons…
• That consequently, Korean cosmetic surgery patients tend to choose from a limited number of (positively-associated) procedures that tend to make them look more Caucasian (or, more accurately, a heavily Caucasian-influenced, Westernized, increasingly global ideal) than Asian, rather than the other way round (with the proviso that “Caucasian” and “Asian” are largely social constructs).
In other words, they can still retain Caucasian beauty ideals despite not wanting to look Caucasian personally.
Caveats abound. One of the most obvious of which is that it sounds like I’m saying any empowerment patients feel—and most do feel empowered—is really a sense of false consciousness, their choice of positively-associated procedures really being heavily circumscribed by society, their surgeons, and themselves. I’m very wary of any notion of consumers as dupes though, so I was glad to stumble across the work of Kathy Davis for an opposing viewpoint, as described in Body Image: Understanding body dissatisfaction in men, women, and children by Sarah Grogan (2nd ed., 2007). Yet she too acknowledges empowerment still occurs within the context of culturally-limited options (page 70, my emphases):
The question of why women are willing to undergo unnecessary surgery to make their bodies conform more closely to accepted norms may help us to understand the nature of body dissatisfaction in women. Kathy Davis (1995) in Reshaping the Female Body: The Dilemma of Cosmetic Surgery looks at cosmetic surgery from a broadly feminist viewpoint. She argues that understanding why women engage in a practice which is painful and dangerous must take women’s explanations as a starting point. She attempts to explore cosmetic surgery as one of the most negative aspects of Western beauty culture without seeing the women who opt for the “surgical fix” as what she calls “cultural dopes”(i.e., by taking seriously their reasons for having cosmetic surgery).
Page 71:
Women she interviewed [in the Netherlands] reported that they experienced the decision to have cosmetic surgery as a way of taking control of their lives, and that cosmetic surgery was something that they had decided upon for themselves, rather than under pressure from partners or knife-happy surgeons. They were clear that they had made informed choices, based  on weighing up the risks and possible benefits of surgery. Davis takes the position that cosmetic surgery may be an informed choice, but it is always made in the context of culturally limited options. She argues fiercely against the idea expressed by many authors, including Kathryn Morgan (1991), that women who opt for cosmetic surgery are victims of male lovers, husbands, or surgeons. She also disagrees that women who opt for cosmetic surgery are the dupes of ideologies that confuse and mystify with the rhetoric of individual choice.
on weighing up the risks and possible benefits of surgery. Davis takes the position that cosmetic surgery may be an informed choice, but it is always made in the context of culturally limited options. She argues fiercely against the idea expressed by many authors, including Kathryn Morgan (1991), that women who opt for cosmetic surgery are victims of male lovers, husbands, or surgeons. She also disagrees that women who opt for cosmetic surgery are the dupes of ideologies that confuse and mystify with the rhetoric of individual choice.
Davis (1995) sees women as active and knowledgeable agents who make decisions based on a limited range of available options. She argues that women see through the conditions of oppression even as they comply with them. The women she interviewed reported that they had made free choices, although these “choices” were limited by cultural definitions of beauty and by the availability of particular surgical techniques. The “choices” need to be placed within a framework that sees women’s bodies as commodities.
But the specific journal article which inspired this post is “Medicalization of Racial Features: Asian-American Women and Cosmetic Surgery,” Medical Anthropology Quarterly 7(1), pp. 74-89, March 1993 by Eugenia Kaw, which I read on pages 167-183 of The Politics of Women’s Bodies: Sexuality, Appearance, and Behavior, ed.by Rose Weitz (1st edition, 1998; source, above-right). Originally, I intended to summarize it for you here, but since I’ve started writing I’ve found a PDF of the article, so frankly I see no need—interested readers can just download it and read it for themselves. Instead, let me provide some copy and pastes here to give the gist for any much-too-busy-but-still-quite-interested readers.
First, from page 79, on the negative associations of “Asian” features:
 From page 81 on the how the medical industry legitimizes and perpetuates those negative associations:
From page 81 on the how the medical industry legitimizes and perpetuates those negative associations:
 Finally, from pages 85-86, on the clear patterns that emerge despite patients making “truly individual choices” (alas, Kaw too is guilty of casually throwing in that 50% figure!):
Finally, from pages 85-86, on the clear patterns that emerge despite patients making “truly individual choices” (alas, Kaw too is guilty of casually throwing in that 50% figure!):
 Again, caveats abound. Not only is Kaw’s article quite dated, but there are dangers in extrapolating studies based on Bay Area surgeons and patients to Koreans (to be clear, Kaw herself never does so). As Ruth Holliday and Jo Elfving Hwang explain in “Gender, Globalization and Aesthetic Surgery in South Korea,” Body & Society, June 2012 18: 58-81 (page 7 at this downloadable link):
Again, caveats abound. Not only is Kaw’s article quite dated, but there are dangers in extrapolating studies based on Bay Area surgeons and patients to Koreans (to be clear, Kaw herself never does so). As Ruth Holliday and Jo Elfving Hwang explain in “Gender, Globalization and Aesthetic Surgery in South Korea,” Body & Society, June 2012 18: 58-81 (page 7 at this downloadable link):
In researching cosmetic surgery in Korea, a further problem of ‘ethnic’ cosmetic surgery studies which focus on Asian-Americans is that their results have been generalized to apply to ‘countries of origin’; that is, Koreans in Korea. Accordingly, what are seen as ‘whitening’ practices in the West are also presented as ‘Westernizing’ practices in the East without much consideration of localized discourses that intersect with more globalized practices of cosmetic surgery. Explanation of Korean cosmetic surgery only in terms of Westernization seems unlikely given Korea’s strong sense of nationalism, as well as its national relationship with other regional powers, for example, Japan.
Indeed, their article is a real eye-opener in its own right (no pun intended!), and made me realize how Korean cosmetic surgery is even more complicated than I imagined, and how much more I have to learn. For example, from page 13 (source, below-right):
Blepharoplasty [eyelid surgery] in particular has often been explained in terms of ‘Westernization’. However, it is worth remembering that whilst many Koreans already have a double eyelid, many Westerners undergo blepharoplasties too. Wider eyes signal youth, energy and alertness. Korean women have used temporary eyelid tapes and glues for decades, most usually justified as easing the application of make-up. Eye surgery is seen as a more convenient permanent fix (the surgery takes ten to twenty minutes depending on technique) which saves time and allows greater participation in sports and swimming, for example. Blepharoplasties (like breast augmentations)  appear to have originated in Japan (the first performed by a surgeon named Mikamo in 1896) and were originally used to treat children born with one single and one double eyelid (Miller, 2006). East Asians tend to have more adipose fat in the eyelid than Caucasians and importantly men and women who have too much fat removed are seen negatively as artificially western. Wider eyes may be desirable, but they must be wider Korean eyes, not Western ones. The most important aim of cosmetic surgery is to create a natural look that ‘enhances’ the body without losing the ‘Koreanness’ of the subject who undergoes surgery.
appear to have originated in Japan (the first performed by a surgeon named Mikamo in 1896) and were originally used to treat children born with one single and one double eyelid (Miller, 2006). East Asians tend to have more adipose fat in the eyelid than Caucasians and importantly men and women who have too much fat removed are seen negatively as artificially western. Wider eyes may be desirable, but they must be wider Korean eyes, not Western ones. The most important aim of cosmetic surgery is to create a natural look that ‘enhances’ the body without losing the ‘Koreanness’ of the subject who undergoes surgery.
Like most epiphanies then, this is really a starting point for me rather than the final word, and I realize it may already be familiar to the many readers who’ve done more research into cosmetic surgery than myself (thank you for indulging me!). Nevertheless, I do think that the Korean public and cosmetic surgeons and patients will share many of the same associations as their Bay Area counterparts. And, even if I’m mistaken about that, investigating public associations of and (especially) medical discourses surrounding certain body features promises to be a fruitful new line of investigation for understanding body image in Korea. I’d be very interested and grateful to hear your thoughts on that, and your own observations.
Update: It wasn’t really relevant to the making of this post, but Joanna Elfving-Hwang’s “Cosmetic Surgery and Embodying the Moral Self in South Korean Popular Makeover Culture” in The Asia-Pacific Journal, Vol. 11, Issue 24, No. 2, June 17, 2013, focusing on the Korean show Let Me In, would be an excellent starting point for more on those medical discourses.
Update 2: I’ve been blogging for so long, sometimes I forget what’s already been posted! Please see here for one of my most-heavily commented posts, in which a reader discusses how those negative associations of monolids came about.
Media and Body Image Workshop, Bar Carmen, Seoul, Sunday 23rd, 5-8pm
 (Sources: left; right, “Bunch” by Amanda S. Lanzone)
(Sources: left; right, “Bunch” by Amanda S. Lanzone)
And I’ll be the guest speaker! Please see Disruptive Voices’ Facebook Event page for more details and RSVPs, or if you’re not on Facebook then please feel free to ask any questions in the comments here, and/or to just turn up to Bar Carmen in Itaewon on the day. (Note that it’s not on the main drag though, but on the other side of the hill: see here or here for maps.)
Blogging-wise, unfortunately the timing is terrible sorry: my father-in-law is having a major operation in Seoul in a few days, and my wife will be attending to him, leaving me to look after our children until the night before the workshop. A demanding enough job even when we’re both here, that means that all my spare time will be spent on preparing my presentation (yes, they really do take that long!). So, apologies to readers, and I’ll get back to writing here as soon as I can.
Update, Saturday 22nd: PRESENTATION HAS BEEN CANCELLED — I’m not used to this sort of thing sorry, so I’ll just say it: I’m afraid my father-in-law’s condition has rapidly deteriorated, and there’s a possibility he may not make the night. I’ll keep you posted, but of course I can no longer give the presentation. Sorry everybody, and thanks for understanding.
Update, Sunday 23rd: To clarify sorry, the workshop itself is still going ahead.
My father-in-law is still in critical condition.
Update, Thursday 27th: There were some very scary moments, but I’m happy to say that father-in-law recovered earlier in the week, and is due to be discharged today :)
What? She’s NOT Pregnant??!
 (Sources: left, personal scan; right)
(Sources: left, personal scan; right)
Sorry for the slow posting everyone, admittedly somewhat ironic during the semester break. I’ve just been busy with a lot of offline work recently, and unfortunately for you readers it’s still ongoing.
Also, I’ve been fulfilling a New Years’ resolution to spend much more time in the bedroom with my wife. As in, I’ll turn off my computer at 10pm and lie in bed reading books, while she calls English teachers from her desk alongside me (she’s a recruiter). Now four weeks into 2014, she only occasionally tells me to fuck off back to my study and make more money from writing, so all is good.
One of those books is Seeing Through Clothes by Anne Hollander (1980 ed.), picked up in Nampo Book Alley. Bursting with revelations for — ahem — complete beginners to art-history, I was especially surprised to learn that the woman in Jan van Eyck’s Arnolfini Portrait above-right isn’t pregnant, despite the strong impression of that I’ve had for a good quarter-century or so. So, with apologies for not reading something more Korea-related on this occasion, please allow me to pass on what I’ve learned, starting with pages 109-110 (my emphasis):
Because of the desirable quality of a big female stomach for so many centuries [James — The shift in emphasis to the bosom would come in the late-seventeenth century], pregnancy was not represented in art by showing a distended belly, even in genre scenes. If an unmistakable indication of pregnancy were intended, it seems to have been customary to show an otherwise unwarranted disarrangement of clothing: stays unlaced a little from the bottom for example, or corsets left off entirely and extra loose folds of smock noticeable in front….The swelling abdomen was too conventional a female attribute to be useful for specific references to pregnancy. Giovanna Arnolfini, in Van Eyck’s famous double portrait, often thought to be pregnant, is in fact demonstrating how a young bride’s fashionable slim soldiers and chest might be set off by an equally chic abdominal swell, exaggerated on purpose to display the fur-lined green excesses of her gown. Her own desirability and her husband’s riches both show; a well-known mode of bourgeois female self-presentation.
In this particular style of dress, a woman’s belly provided the central accent point of her costume. It was the place where the balance was struck between elaborate headdresses and dragging skirt — or, for virgins,  between a dragging skirt and a long mane of hair [James — Compare the right panel of the Dresden Triptych, by the same painter; source]. The domelike belly was not only erotically pleasing but elegant; it connoted elegance rather than fruitfulness. In the nude art that corresponds to this kind of fashion, it would also have done so.
between a dragging skirt and a long mane of hair [James — Compare the right panel of the Dresden Triptych, by the same painter; source]. The domelike belly was not only erotically pleasing but elegant; it connoted elegance rather than fruitfulness. In the nude art that corresponds to this kind of fashion, it would also have done so.
More on those last points in a moment. First, given the common false conception (no pun intended) of a pregnant wife, again I was surprised that greater attention wasn’t given to that in the voluminous Wikipedia entry on the painting:
Although many viewers assume the wife to be pregnant, this is not believed to be so. Art historians point to numerous paintings of female virgin saints similarly dressed, and believe that this look was fashionable for women’s dresses at the time.[32] Fashion would have been important to Arnolfini, especially since he was a cloth merchant. The more cloth a person wore, the more wealthy he or she was assumed to be. Another indication that the woman is not pregnant is that Giovanna Cenami (the identification of the woman according to most earlier scholars) died childless,[33] as did Costanza Trenta (a possible identification according to recent archival evidence);[16] whether a hypothetical unsuccessful pregnancy would have been left recorded in a portrait is questionable. As mentioned above, some viewers have argued that the woman in the portrait is already pregnant, thus the protruding belly. Harbison, however, maintains her gesture is merely an indication of the extreme desire of the couple shown for fertility and progeny.[34]
Note 32 leads to Chapter 4, pp.105-6 of The Arnolfini Betrothal: Medieval marriage and the enigma of Van Eyck’s double portrait, by Edwin Hall (1994):
The comparative approach I advocate for elucidating the meaning of the London panel is readily exemplified with reference to the female figure’s supposedly pregnant state. Documented as early as the Spanish royal inventory of 1700, this mistaken inference continues to be drawn by modern viewers seeing the picture for the first time. But among those familiar with Franco-Flemish works of the fifteenth century a consensus has developed that this is not the case, for virgin saints, who obviously cannot be pregnant, also appear gravid in many contemporary representations. The woman in the London panel has thus often been compared with the Saint Catherine in the right wing of Van Eyck’s Dresden Triptych, who is similarly portrayed (Fig. 48), as is the bride in the marriage vignette of Rogier’s Seven Sacraments Altarpiece (see Fig. 21) as well as the Virgin and one of her attendants in Israhel van Meckenem’s Marriage of the Virgin (see Fig. 50). And a protruding belly is seen in many female nudes, including again virgin saints, as in a depiction of the martyrdom of Saint Catherine in the Belles Heures (Fig. 49).[25] Whether or not this feature is explained by fifteenth-century perceptions of idealized feminine beauty, these images clearly reflect some contemporary Flemish convention whose precise meaning is no longer readily apparent.
 (Source)
(Source)
Another revelation from Hollander is that nudes tend to be posed and/or presented as if they were still wearing the fashions of their era, which incorporated sexual standards and symbolism which may no longer apply today (e.g., those “erotically pleasing domelike bellies”). One consequence is that we “may even mistake an erotically intended image [of the past] for an idealized one — if it lacks the shapes, proportions, and details we are accustomed to responding to in contemporary life” (p. 88; this is given as an example). Another is the gravity-defying breasts of the Nude Maja on the cover I scanned; ironically, again something I’m only noticing for the first time (my emphasis; p. 91):
One of the most telling features on the nude maja’s body is that it seems to show the effect of corseting without the corset — which, on the other hand, is very definitely present in the dressed version. The high, widely separated breasts and rigid spine of the recumbent nude lady are as erotic as her pubic hair fuzz or sexy smile. Her breasts indeed defy the law of gravity; and her legs, accustomed to appearing through the lightweight and rather narrow skirts of the day  [James — It was painted circa 1797-1800], are self-consciously disposed for effect, like those of a twentieth-century woman. It is the emphatic effect of her absent modish costume that makes her a deliberately sexual image.
[James — It was painted circa 1797-1800], are self-consciously disposed for effect, like those of a twentieth-century woman. It is the emphatic effect of her absent modish costume that makes her a deliberately sexual image.
And on that note, thank you for the indulgence of any art-history majors still reading, and I’d really appreciate any suggestions for further, much more recent reading on the links between historical and contemporary ideals of body image — or rather, the representations in popular-culture thereof (Ways of Seeing by John Berger {1972} is good of course, but frankly I found the final chapter on that to be its weakest, and of course it’s also old). Naturally, anything on Korea in particular, and for one I’d be interested in hearing if Visualizing Beauty: Gender and Ideology in Modern East Asia edited by Aida Yuen Wong (2012; source) is worth buying for instance, which I’ve been wavering about because it only has two chapters on Korea. Or are there any other possibilities, in Korean (but not this one!) or in English? Thanks!
Disruptive Womyn: Media and Body Image — Presentation in Itaewon this Sunday
 (Source)
(Source)
Minji Kim, founder of the 몸매불문 나되기 / Real Beauty Doesn’t Hurt project, and whom many of you will remember from this post, is giving a presentation at Bar Carmen in Itaewon this Sunday. As explained at the Facebook event page:
Media has had a massive impact on ourselves and how we view and value ourselves. Even when we try to turn a blind eye or are fully aware of the internal system of “media” and all that it entails, the effects and subliminal messages are deeply massaged into our minds.
We live in a world that sends us all sorts of messages about the ‘perfect’ body. We are constantly receiving image related messages from different mediums, both within the media and our surrounding environments, indicating what society views as ‘beautiful’.
Naturally, instead of embracing and celebrating diversity in all body types, we concentrate on a dangerous notion of physical perfection.
While the media provide a necessary and valuable community service to society, the other reality is that media is responsible at times for misleading as well as perpetrating these ‘perfect’ images which are often than not digitally enhanced (airbrushed) and manipulated before final production.
 Ladies, let’s join together to discuss how media has or hasn’t impacted your self-worth. Let’s also discuss the relationship(s) we have with our bodies, our relationships with others, etc.
Ladies, let’s join together to discuss how media has or hasn’t impacted your self-worth. Let’s also discuss the relationship(s) we have with our bodies, our relationships with others, etc.
There will be tea available (for free) and wine and beer for purchase (source, right).
Hope to share in this conversation/discussion with all of you~
And in Korean:
우리는 외형적 “완벽함”을 요구하는 사회에서 살고 있습니다. 미디어 외 여러 매체를 통해 우리 사회로부터 인정받는 전형적인 “미인”이 무엇인지, 나아가 여성으로서의 값어치를 외형으로 측정받는다는 메세지를 매일 일상 속에 끊임 없이 받고 있습니다.
이렇듯, 개개인이 가지고 있는 다양한 몸매를 존중하고 축복하지 못하고 우리는 미디어와 사회에서 제시하는 위험한 ‘완벽한 외모’를 쟁취하기 위해 힘을 쏟습니다.
미디어는 우리 사회에 여러 필요하고 가치있는 서비스 및 정보를 제공해주는 역할을 함과 동시에 포토샵 및 디지털 편집으로 왜곡된 “완벽한” 이미지들을 대중에게 강요하는 역할도 하고 있습니다.
여러분! 다른 여성들과 함께 <Media and Body Image> 에 대해 이야기 함께 나누면 좋겠습니다. 사회 속 미의 기준이 우리에게 어떻게 영향을 미쳤으며 미치고 있는지 나아가 우리의 미래를 위한 발걸음을 어떻게 나아갈 것인지 의논해봅시다.
See the link for further details, or alternatively the project’s blog or Facebook page (both in Korean).
Korean Sociological Image #82: Pink it and shrink it!
 (Source: Brand New Day)
(Source: Brand New Day)
Hello everyone, I’m James. I’m 37, male, cisgender, and heterosexual. And I love pink.
It started innocently enough. As “The Korean Gender Guy”™, some splashes of it seemed appropriate here and there. Hence the pink hyperlinks and image borders on the blog in recent months.

Then, as a father of two young daughters, I realized I needed to embrace it for their sakes. On the one hand, to demonstrate that it’s not just a girls’ color, so they in turn would be more open to the blue side of the toy aisle. On the other, to make it so uncool, unfeminine, and/or ugly in their eyes that they’d be put off it for the remainder of their childhoods and adolescence, with all the gender socialization that comes with it.
Mostly this meant things like fighting over rare pink game tokens, and drawing a lot of pink planets and rockets for “Extra Burn!”™ our own handmade, much improved version of snakes and ladders. Later, whenever it was an option, pink would also become the default choice for things we bought when out shopping together, like a kitchen tray, or Xylitol gum that came in a pink shiny bag.
Still, there was nothing that couldn’t be forgiven for a guy living with three females. But done so often, it soon became automatic, even for things just for myself. Before I knew it, I’d be leaving for work with my cute pink umbrella, pink socks under my black work pants, pink-tinted sunglasses still in my bag (bought in New Zealand, but which I’d been assured were “just too dam gay” to wear there); pink folders for my class plans; phone with pink  cover, and neon-pink headphones for my MP3 player. On the subway, I’d take advantage of the wifi to check on the delivery progress of a pink suitcase I’d just bought online, rationalizing my choice by telling myself that the color would make it easier to spot at airports.
cover, and neon-pink headphones for my MP3 player. On the subway, I’d take advantage of the wifi to check on the delivery progress of a pink suitcase I’d just bought online, rationalizing my choice by telling myself that the color would make it easier to spot at airports.
So, when the inevitable confrontation came, from a visibly uncomfortable male friend, I admit I shared his double-take. In my case though, I realized I looked…well, just fabulous actually, and wondered what else I could add.
Something drastic had to happen soon. Otherwise, who knows what depths of depravity I would have sunk to?
Fortunately, a reality check was recently provided by Lotte Chilsung through Song Hye-Gyo, who reminded me that I was the wrong sex to enjoy “Icis 8.0,” their latest bottled water…
(“Healthy under-eye areas? Pink! Healthy cheeks? Pink! Healthy fingertips? Pink! Healthy lips? Pink! So…how about healthy water? Invigorating pink energy! Icis 8.0!”)
Squarely aimed at women in their 20s and 30s, alas, I’ve been unable to find a source explaining the rationale behind its pink-centered marketing campaign, and am especially confused about how a pH of 8.0 would be pink exactly (my understanding is that it would actually be blue?). However, I did find the following article on very similar examples of gendered marketing, which I think provides some insights. That is to say, it’s clearly an advertorial on the one hand, but on the other I think no exaggeration or misrepresentation of their marketers’ rationales either, the sheer bullshit required to market something like water to just one sex being nothing short of astounding. Yet, in hindsight, utterly predictable too.
“여자들만 드세요” 여성전용 식음료 제품들 ‘눈길’ “Women Only”: Eye-catching food and drink products exclusively for women
Betanews, 14/09/2009, 이직 기자 (leejik@betanews.net)
여자의 손길을 얼만큼 많이 받느냐에 따라 생사여부가 결정되는 곳이 식음료 시장이다. 관련 기업들은 여성의 감성을 자극하기 위하여 장동건, 정우성, 알렉스 등 한 시대를 풍미하고 있는 ‘훈남’들을 광고 모델로 내세운다. 하지만 정작 여자의 마음은 남자보다 여자가 더 잘 아는 법이다. 이를 반영하듯이 최근 ‘I’m Woman!’을 선언한 여성전용 컨셉 제품들이 잇따라 출시되고 있어 눈길을 끌고 있다.
The food and drink marketplace is where products with a woman’s touch will succeed or fail. Some companies have used currently popular handsome men like Jang Dong-gun, Jung Woo-Sung, and Alex Chu to appeal to women. However, in real life, women know women’s hearts and minds much better than men. With this in mind, several companies have launched products following an “I’m a Woman!” concept.
 (Source; sources far above — unknown)
(Source; sources far above — unknown)
파나블루 ‘슈어’ – 피부에 좋은 미네랄 성분, 여자 손에 맞는 용기 디자인, Pink & Purple 컬러.
Panablu’s “Sure” — [A water drink] with mineral components good for the skin, and in a pink and purple container that fits perfectly into women’s hands.
국내1호 해양심층수 기업 파나블루(http://www.panablu.co.kr / 대표 설동환)는 올 여름 여성을 위한 뷰티(Beauty)워터 ‘슈어(SURE)’를 출시했다. 슈어는 물의 성분부터 용기 디자인까지 철저하게 여성을 형상화 한 제품이다.
Panablu is the first domestic company to sell mineral water sourced from the ocean depths, with company representative Sol Dong-Hwan explaining that Sure was launched this summer for women’s beauty. From the mineral components to the container design, it is a product thoroughly designed for women.
[James: Panablu wasn’t the first — Lotte Chilsung was using Olympic swimmer Park Tae-Hwan to sell “Bluemarine” at least a year before the first news reports about “Sure” I can find.]
슈어는 세계 최고 깊이인 수심 1500m의 해양심층수로 여자 피부에 좋은 미네랄이 일반 먹는샘물 제품 보다 10배 이상 함유되어 있는 ‘여자의 물’이다. 용기 디자인도 여성의 S 라인과 바다의 물결을 형상화 한 아름다운 곡선이 물병 전체를 감싸고 있다. 하지만 이 곡선은 단지 미(美)를 표현한 것만은 아니다. 신비스러운 여자의 신체 비밀도 담겨 있다. 이 물결 무늬는 20~30대 여성 300명을 대상으로 실시 한 ‘보틀 핸드프린팅 테스트(bottle hand printing test)’의 결과로 여자 손에 가장 편안한 그립감을 안겨줄 수 있게끔 디자인 된 것이다.
Sure water is taken from a depth of 1500m under the sea, the greatest depth of any mineral water source, and this “women’s water” contains 10 times more minerals that are good for women’s skin than regular bottled waters. Also, the curve of the bottle beautifully captures both the swell of sea waves and women’s S-lines. However, it doesn’t just visually capture their beauty — it also holds the secrets to their mysterious bodies [James: *Cough*, *Splutter*]. It was tested on 300 women in their 20s and 30s in a “bottle hand printing test,” and they selected it as the most convenient and comfortable to grip and hold.
파나블루 마케팅팀 이만 팀장은 “먹는샘물 시장 조사 결과 휴대용 물을 구입하는 소비자 가운데 80% 이상이 여성이었다”면서 “이에 맞춰 슈어는 여성 몸에 꼭 맞는 물의 성분과 그립감 뿐만 아니라 기본 색상도 그동안 생수 제품에 많이 사용되어 왔던 블루(Blue)계열 대신 핑크앤퍼블(Pink & Purple)톤을 채택하게 되었다”고 말했다.
Panablu marketing team manager Lee Man said, “The results of a survey of the bottled water market showed that over 80% of consumers were women,” and that “Sure is not just a product with a grip and components perfectly designed for women’s bodies, but so too were the colors pink and purple chosen rather than the blue which most bottled waters have.”
[James: Strangely, hourglass-shaped bottles have also been claimed to be the perfect shape for women’s hands, and indeed Icis 8.0’s ribbed bottle too.]
 (Sources: HiteJinro, ThinkFood)
(Sources: HiteJinro, ThinkFood)
하이트맥주 ‘S’ – 여자를 위한 저(低)도수, 저칼로리, 식이섬유 첨가로 장 운동 촉진까지
Hite “S Beer” for Women — Low alcohol level, low calories, added fiber, designed to aid bowel movements
하이트맥주는 올 여름 여대생 홍보대사를 대대적으로 모집하는 등 ‘여성’과 ‘S라인’에 컨셉을 맞춘 여성전용 맥주 ‘S맥주’의 마케팅 활동을 대폭 강화했다. S맥주는 식이섬유 첨가, 저 칼로리, 저 도수, 매혹적인 에메랄드 빛깔 용기, S라인 모양의 전용 잔 등 여러모로 여성을 닮은 맥주다.
This summer, Hite Beer recruited female university students on a grand scale to market “S Beer,” a beer designed for women combining the concepts of “woman” and “S-line.” S Beer as added fiber, low calories, low alcohol content, a seductive emerald bottle, with glasses in S-line shapes that resemble women’s bodies in many ways.
[James: These are the glasses referred to (has anyone seen one in real life?). In contrast to those claims about them, much of the early marketing for the product — when this article was written — seemed to center on how much women’s bodies could resemble the bottles rather than vice-versa, such as on the left above.]
S맥주에는 여성에게 꼭 필요한 식이섬유가 다량으로 함유되어 장 운동을 촉진시키고 체형관리에 도움을 준다. 칼로리도 100ml당 40~50kcal인 다른 맥주와 달리 30kcal로 낮춰 다이어트 하는 여성도 부담 없이 마실 수 있도록 했다. 평소 술을 잘 못하는 여성을 고려해 알코올 도수도 4.0%로 낮췄다.
S Beer has a large amount of the fiber absolutely essential for women, and through aiding bowel movements helps them to maintain their figures. Whereas most beers have 40-50 kcal per 100ml, this has been reduced to 30 kcal in S Beer, allowing even women on diets to drink it freely. Also, the alcohol content has been reduced to 4.0%, making it suitable for women who can’t usually drink.
이 외에도 국내에서는 처음으로 용기 전체에 매혹적인 에메랄드 컬러를 적용해 세련된 느낌을 표현했다. 가장 눈에 띄는 것은 S맥주의 전용 잔으로 ‘S라인’으로 날씬하게 굴곡진 여체를 형상화 한 점이 특징이다.
In addition, S Beer is the first domestic beer to have a seductive, emerald-colored bottle, giving off a sophisticated feeling. But the most notable thing are the exclusive glasses, slender and curved in the shape of a woman’s S-line.
 (Source: Ncyberzone)
(Source: Ncyberzone)
파리바게뜨 ‘로얄푸딩’ – 작고 투명한 유리병이 핸드백에 쏙… 휴대성 높이고, 칼로리 낮추고
Paris Baguette’s “Royal Pudding” — With a small, clear glass container, just drop it in your handbag…high portability, low calories
파리바게뜨는 2030 여성들을 위한 유럽식 프리미엄 디저트 ‘로얄푸딩’을 출시했다. ‘로얄푸딩’은 신선한 우유와 달걀, 카라멜 시럽이 독특한 맛의 조화를 이루는 제품이다. 입안에 넣는 순간 여느 푸딩에서 맛 볼 수 없는 부드러움과 달콤함을 느낄 수 있다. 하지만, ‘로얄푸딩’은 달콤한 맛에 비해 칼로리는 낮다. 80g 제품 한 개 당 칼로리는 140kcal로 일반 테이크 아웃 카페라떼의 칼로리(300kcal) 보다 저 열량을 자랑한다.
Paris Baguette has launched its premium, European-style desert “Royal Pudding,” aimed at 20 and 30-something women. Royal Pudding is a product with a taste that has achieved a unique harmony of fresh milk, eggs, and caramel syrup. Unlike most puddings, you can taste the softness and sweetness as soon as you put in your mouth. Yet despite that sweetness, it is low in calories. It boasts only 140kcal per 80g, whereas a takeout cafe latte has 300kcal [James: Granted. But how big would that latte be?].
‘로얄푸딩’의 용기는 작고 귀여운 숙녀를 닮았다. 그래서 여성들의 큰 호응을 얻고 있다. 한 손에 잡히는 투명하고도 깜찍한 용기는 시각적 만족감과 함께 핸드백 속에도 부담 없이 들어가 휴대의 편리함을 높였다.
The Royal Pudding container resembles a small, cute lady, so it has a wide appeal to women. Conveniently fitting in one hand, the small, cute container is highly portable. It can be simply dropped in a handbag and carried without a thought.
 (Source: 하하하)
(Source: 하하하)
대상웰라이프 ‘닥터클로렐라S’ – 여성전용 클로렐라 제품, 복용 간편하고 변비와 피부미용에 효과
Daesang WellLife “Dr. Chlorella S” — A chlorella product for women, an easy, effective medicine for constipation and skin beauty
대상웰라이프의 ‘닥터클로렐라S’는 외부 이동이 많고 바쁜 커리어 우먼을 위한 여성전용 클로렐라 제품으로 성분부터 형태까지 여성을 중심에 두고 만든 건강기능식품이다. 닥터클로렐라S에는 ‘락츄로스’가 첨가되어 직장인 여성에게 많이 나타나는 스트레스로 인한 만성 소화불량과 변비를 해소하는데 도움을 준다. 또한 각종 식물성 영양성분을 비롯한 식이섬유질이 들어있어 업무에 지친 직장인 여성들의 피부 건강을 회복하는데도 효과적이다.
From its mineral components to its shape, Daesang WellLife’s Dr. Chlorella S is a chlorella product with many health functions centered on career women who are often on their feet. Dr. Chlorella S contains added lactulose, which helps relieve the stress and chronic digestion problems and constipation which many career women suffer from. It also has many vegetable nutrients and added fiber which is effective for recovering the health of tired women workers’ skin.
닥터클로렐라S의 포장은 개별 낱개 형식으로 가볍고 부피가 작아 여성들이 시간과 장소에 구애 받지 않고 복용할 수 있도록 구성되어 있다. 또한 제품의 형태도 목 넘김과 소화 시킬 때 부담이 적고 장에서의 흡수가 빨라 여성들이 선호하는 과립형으로 만들었다.
Dr. Chorella S consists of small, light pills that are easy to take wherever and whatever you’re doing [James — It also came in powdered form]. The shape makes them easy to swallow, with the granules inside, which are quickly absorbed in the intestines, making them women’s preferred choice.
[James — Judging by the lack of news articles and blog posts after 2009, Dr. Chlorella S was a failure. I’m guessing, because it wasn’t pink? ㅋㅋㅋ]
파나블루 마케팅팀 이만 팀장은 “전통적으로 여성 소비자들에게 성공한 브랜드는 향후 브랜드 확장을 할 때 비교적 쉽게 안착할 수 있었다”면서 “식음료 시장에서 브랜드 확장이 활발하게 이뤄지고 있다는 점을 감안한다면 여성전용 식음료 제품은 앞으로도 꾸준히 출시 될 것”이라고 말했다.
Lee Man, the Panablu marketing team manager, said “Brands that were traditionally successful with female consumers could relatively easily reach them when they wanted to expand,” and that “In the food and drink product, many brands are actively considering women-targeted products. Expect to see many more of them in the future.” (End)
 (Sources: hayena2000, Vingle)
(Sources: hayena2000, Vingle)
Before I forget, sorry again for the slow posting everyone, but I was very busy at work, and caught a frustrating, lingering cold. Meanwhile, have any readers encountered similar gendered campaigns for unisex products, in Korea or overseas? Also, how do any parents among you deal with your children’s attitudes to pink and blue? Please let me know!
p.s. I wasn’t joking about my own, “pink strategy” in the introduction, or about any of my purchases. I really do think I look fabulous with them! :D
Update: I forgot to mention these his and her “V-line” face-shapers, the ads for which can be seen almost on every other website at the moment (if you live in Korea).

 Also, management company E-tribe contracted their girl-group Dal Shabet to endorse the product. Such endorsements by Korean Wave stars likely play a strong role in the propagation of Korean beauty ideals overseas:
Also, management company E-tribe contracted their girl-group Dal Shabet to endorse the product. Such endorsements by Korean Wave stars likely play a strong role in the propagation of Korean beauty ideals overseas:
- Korean Sociological Image #64: Hourglass-shaped Drink Bottles
- “Body Changing” Diet-Drink Generously Donated to High School Students
- Korean Sociological Image #54: Sex & Drugs
- Gender Advertisements: What, boys can drink girly drinks now?
- Korean Photoshop Disaster #8: The 100% Korean Lady Burger
- Korean Sociological Image #15: Gendered Health Drinks
- Korean Sociological Image #2: Son Dambi’s Corset
- Gendered Tea-drink Advertising in South Korea (Updated)
- Gender Socialization (Category)
(For more posts in the Korean Sociological Image series, see here)
Korean Sociological Image #80: Fashion’s Complete Body!
Sometimes, I wonder if I exaggerate Korea’s alphabetization craze. Then I come across advertisements like this one:
 The advertisement on the left reads:
The advertisement on the left reads:
Tight chestline, Sleek braline; Slender waistline, No-cellulite bellyline; and Attractive y-line, Smooth legline. Fashion’s Complete Body! Summer Event. 10% Event Discount.
I couldn’t have put it better myself.
Please see here and here if this is the first you’ve heard of “alphabetization” though, with the latter link focusing on Western historical parallels and the Y-line specifically. Alternatively, see here for more on the physically impossible X-line!
(For more posts in the Korean Sociological Image series, see here)
Busan Slutwalk, Sat Aug 31, 6-7PM, hosted by Don’t Do That
Update: I’ve just been informed that Slutwalk Korea and Don’t Do That are very different organizations, and that the latter — the organizers of Saturday’s event — advocate wearing more conservative dress than in regular slutwalks, arguing that participants who wear racier costumes run the risk of being charged with indecent exposure, and that toning things down would be more appropriate for a first event in Busan. Nevertheless, they accept short miniskirts, hotpants, croptops, and whatever slogans participants wish to write on placards.
Apologies if I’ve inadvertently misrepresented either organization, and I’ll update readers if any new information becomes available. Alternatively, please also check Korean Gender Café or Don’t Do That’s (Korean) Twitter feed.
Update 2: The Korea Times discusses the disagreements between the two organizations here, saying Slutwalk Korea has accused Don’t Do That of slut-shaming itself in its emphasis on conservative dress. I don’t know enough about either organization to comment sorry, but wager that any such accusation will have been greatly exaggerated to better fit the snarky tone of the article.
Original Post:
Reblogged with permission from Korean Gender Café:
Don’t Do That Campaign welcomes you to participate in a slut walk
I had a great chat today with organizers of Don’t Do That (성범죄인식개선캠페인 돈두댓), a campaign to change mindsets about sex crimes. The group is organizing a slut walk campaign in Busan and Seoul. I translated the information below and hope that readers will share it widely.
Don’t Do That is a voluntary group that comes together to raise awareness about sex crimes. Their site offers a lot of information and is a great resource.
Event in Busan:
On Saturday, August 31, 2013, 6PM ~7PM there will be a slutwalk hosted by the Don’t Do That (성범죄인식개선캠페인 돈두댓) Busan Team.
The walk will take place near Bujeon-dong, Seomyeon Subway Station (Line 1 & 2), Exit 1.
Participants will meet at the ally next to Judies Taehwa and march toward Lotte Department store. Please see the map below and spread the word~
For additional information about this event, please contact organizers via KakaoTalk ID jinamarna or via Facebook.
Here is a little map I made of the area in Busan where the slut walk will take place:
 This is an image I found of Judies Taehwa storefront, participants will meet nearby at 6PM:
This is an image I found of Judies Taehwa storefront, participants will meet nearby at 6PM:
 For more information about Don’t do that (성범죄인식개선캠페인 돈두댓) please check them out on Facebook, Twitter, and Daum Café.
For more information about Don’t do that (성범죄인식개선캠페인 돈두댓) please check them out on Facebook, Twitter, and Daum Café.
Busan readers, if you attend the event, I would really love to hear about it~ I wish I could make it out this time, but I can’t. Please share this event and support the cause.
Readers in Seoul, I will be sure to provide similar translation/map when I hear from the Don’t Do That Seoul Team.
Another group that may interest readers is Slutwalk Korea. Slutwalk Korea organized the first slutwalk movement in Asia in early 2011. They launched a number of events in global solidarity with the slutwalks that started in Toronto and all over the world that year. They have also hosted global solidarity events for Pussy Riot and on March 8, 2013 for International Women’s Day. They have a great Twitter feed and regularly post information related to sexual violence or slutwalk-type events in Korea ( I learned about Don’t Do That from a Slutwalk Korea Twitter post).
Posted by Chelle B. Mille.
(See here for a write-up of the 2011 Seoul event by Roboseyo, or the “잡년행진” tag and “Rape” and “Sexual Harassment” categories for related posts on this blog)
Update 3: Here’s a report of the event, written by one of the participants.
Guest Post: Challenging Korea’s Body Image Paradigm
 (Source)
(Source)
If you are a person living in Korea, you are likely to have had your weight or appearance commented on. “You have gained/lost weight!” is a customary greeting. Dieting is the most common topic for daily conversations. Ads promote unrealistic beauty standards for both women and men. Worse, if you don’t look like them, you are likely to be discriminated against or dismissed as some who needs to get some work done. Self-love is prohibited unless you look like a Barbie doll. There are voices and messages everywhere, both internally and externally, that arouse insecurity around your looks. Body-policing is a common practice.
 Overwhelmingly obsessed with thinness, I dare to call Korea an eating-disordered society. I know this because I have been struggling with eating disorders for 9 years, now marching on the road to recovery. Living here, staying on the recovery-track is extremely difficult because all the internal eating-disordered voices and negative self-talk, which I have worked so hard to detach myself from, become real external voices to attack my vulnerable psychological wounds. On the other hand, recovering from eating disorders in this country is double-strengthening my immunity to these eating-disordered voices. I am well-aware of how self-destructive and unproductive these voices are, and how I can protect myself from them.
Overwhelmingly obsessed with thinness, I dare to call Korea an eating-disordered society. I know this because I have been struggling with eating disorders for 9 years, now marching on the road to recovery. Living here, staying on the recovery-track is extremely difficult because all the internal eating-disordered voices and negative self-talk, which I have worked so hard to detach myself from, become real external voices to attack my vulnerable psychological wounds. On the other hand, recovering from eating disorders in this country is double-strengthening my immunity to these eating-disordered voices. I am well-aware of how self-destructive and unproductive these voices are, and how I can protect myself from them.
But, what about those who haven’t been consoled? So many Korean people, especially women of all ages, believe there is no other way to be loved or socially recognized without dieting or getting plastic surgery. Men believe women should naturally look like the ready-made Barbie dolls in fashion magazines or entertainment shows when they are in fact extremely unrealistic. I guarantee there is not a single woman in this country who hasn’t felt insecure about her looks or body parts. Under such circumstances, women and men are likely to fall victims of eating disorders. Statistical data can’t speak for the reality because people are not even aware that these voices are ‘disordered’ voices. Obsession with thinness, extreme dieting, judging others by appearance and feeling insecure about their natural looks feel too ‘normal’ for people to acknowledge them as problems. Walking on the streets, I would hear fat talk or negative self-talk 99% of the time. These voices kill me, even more so to realize that there are so many souls who are suffering from from-mild-to-severe forms of eating disorders but are not even aware of it (Source above — unknown; source, below).
 The need for body image activism in Korea is dire, for the consequences of continuing the eating-disordered talks in public are obviously disastrous, both for individuals and the society. So, I have brought the Operation Beautiful campaign to Korea to counter the prevailing negative self-talks. I have been posting about it on my (Korean) blog Your Stage is the World, Not the Scale, along with my personal stories of overcoming struggles with distorted body image as well as critiques on dieting ads that make one feel insecure. I am working on compiling these stories to publish a book under the title, Surviving Eating Disorders Where Barbie Dolls Reign Supreme (but I think this will take decades). Currently, I am planning workshops for improving body image, to create safe space to talk about struggles with negative body image, to promote body diversity (healthy-at-every-size approach) and media literacy. I don’t want to force people to stop dieting and start loving themselves immediately. Instead, the most ultimate goal for all these activities is to give people agency over their own bodies and self-esteem, which will allow people to see what really matters and what is there to enjoy in life regardless of how they look.
The need for body image activism in Korea is dire, for the consequences of continuing the eating-disordered talks in public are obviously disastrous, both for individuals and the society. So, I have brought the Operation Beautiful campaign to Korea to counter the prevailing negative self-talks. I have been posting about it on my (Korean) blog Your Stage is the World, Not the Scale, along with my personal stories of overcoming struggles with distorted body image as well as critiques on dieting ads that make one feel insecure. I am working on compiling these stories to publish a book under the title, Surviving Eating Disorders Where Barbie Dolls Reign Supreme (but I think this will take decades). Currently, I am planning workshops for improving body image, to create safe space to talk about struggles with negative body image, to promote body diversity (healthy-at-every-size approach) and media literacy. I don’t want to force people to stop dieting and start loving themselves immediately. Instead, the most ultimate goal for all these activities is to give people agency over their own bodies and self-esteem, which will allow people to see what really matters and what is there to enjoy in life regardless of how they look.
The movement is only fresh. I am aware that social change doesn’t come easily or fast. However, I have a strong faith that by transforming ourselves, we can transform the society we live in. We individuals construct the society; we are not to be constructed by it. We are active agents. I want to tell my stories to you and listen to yours. I am collecting personal stories of struggles with negative body image or external pressure to conform to the unrealistic standards of beauty. Then, I want to open up off and online discussions on how we want to redefine beauty that suits us healthily. Hopefully, we can remind each other how beautiful our bodies are just the way they are; encourage each other to love our own bodies instead of fitting ourselves to someone else’s standards to get approval.
Please share your thoughts, stories, comments, anything you want to say about this movement. Thank you!
Minji.
Talking Points: From Music Downloads to Sweaty Crotches
 (Source: Alyssa Korea)
(Source: Alyssa Korea)
Sorry for the lack of posts everyone. I’ve been absentmindedly researching many, not realizing that I hadn’t put pen to paper for a while. To remedy that, here’s some interesting links that add new information to previous posts of mine, but which didn’t really justify separate updates by themselves:
1. Will saving Korea’s music business end up killing it?
 In an endnote to my recent “Why the Japanese Don’t Illegally Download Music. Much.” post, I wrote:
In an endnote to my recent “Why the Japanese Don’t Illegally Download Music. Much.” post, I wrote:
Like most articles praising the rapid rise of the Korean digital music market and the supposed success of Korean anti-piracy efforts, this article completely fails to mention how absurdly cheap Korean digital tracks are, as noted by Bernie Cho in the opening quote.
The next week, Yim Seung-hee at the Korea Joongang Daily wrote one of the most comprehensive articles on the Korean digital music market yet, noting a lot of resistance to government law changes aimed at raising prices. Here are just a few of the quick factoids to take away from it (source, right):
- Music in Korea used to cost 73 won per download before the changes. That has now risen to 110 won, which is still less than one-tenth what iTunes costs.
- Gangnam Style only earned 3.6 million won in online royalties in Korea, coming from 2.86 million downloads and 27.32 million streams, which works out to an average of about 10.7 won per download and 0.2 won per stream.
- However, in the US, Psy received the equivalent of 2.8 billion won for 2.9 million downloads.
- Meanwhile, one estimate says that the average indie musician earns just two-to-three-million won a year (about the same as most expat English teachers make per month).
- Streaming accounts for 74 percent of online music spending in Korea (probably because of Korea’s ubiquitous broadband wifi), and downloads continue to fall. In contrast, in the rest of the world downloads dominate, making up 71 percent of the online market.
2. “Gaijin”
Leah of The Lobster Dance is featured in a (heavily-commented) Tofugu article about the usage of the word “gaijin,” which she has used in the past but now rejects. It begins:
Gaijin (外人, short for 外国人), or “foreigner” in Japanese, is a complicated word that means a lot of different things to a lot of different people.
Some people take the word lightly; when the Tofugu team was in Japan and a roller coaster we were riding unexpectedly malfunctioned, we joked that it was because the ride wasn’t designed to hold the weight of our giant gaijin bodies.
But for some people in Japan, “gaijin” can be a hurtful and alienating word. It can mean refusal of service at businesses, a barrier to entry for housing, or even threats of harassment or violence.
I thought that I’d reach out to some bloggers living in Japan to see what their thoughts on the word “gaijin” were. I got a lot of great, varied, and nuanced responses.
See “Korean Sociological Image #46: The Language of Exclusion” for a similar discussion surrounding the Korean term waegookin, or “foreigner,” with links to many other posts on the subject in the Korean blogosphere (as of 2010).
3. A Tasteless Ad, or Brilliant Marketing?
Johnny Walker is capitalizing on the 40th anniversary of Bruce Lee’s death by rendering him in CQI for a Blue Label commercial:
The ad features a startlingly lifelike computer-generated rendering of the revered martial-arts star, who died four decades ago. It has sparked ire among fans, who argue that Mr. Lee was a teetotaler and abstained from drinking alcohol for most of his life.
Critics see Mr. Lee’s personal stance as incongruous with an endorsement for a brand whose blended Scotches sell for more than $200 a bottle.
Johnnie Walker has defended the ad, saying it worked closely on it with Shannon Lee, Mr. Lee’s daughter.
Ms. Lee, meanwhile, told the Journal that while her father wasn’t a drinker, he didn’t think drinking was immoral. She also thought the video would be an “innovative way to get my father’s ideas out.”
See Scene Asia for the rest, or my “Raising the Dead: The Future of Advertising?” for a much better example featuring Audrey Hepburn, and many others in the comments (readers made me realize using dead celebrities in ads was surprisingly common). As for this example, I share The Ethical Adman’s criticisms that “there’s something really disturbing about dead celebrities being recreated to sell brands,” and that “it seems like the ultimate violation of a person’s integrity, at a time when they cannot even defend themselves.”
Most of all, I think it was incredibly hackneyed to use a teetotaler to sell alcohol, no matter how famous he was. And I just can’t believe how incredibly bad the CGI is, despite the accolades.
 (Source: Unknown)
(Source: Unknown)
4. Lee Hyori for “Dazed and Confused”: Appropriation or Appreciation?
See Audrey Magazine or Omona They Didn’t! for the details. Or, for a similar example by T-Ara last year, see “Thinking through Korean Appropriation of American Indians” at Sociological Images, which I made a big contribution to.
https://twitter.com/rjkoehler/status/359197611481239552
Meanwhile, I’m going to buy a copy to see if there was any rationale to that “vulgarity,” which I find rather charming myself…
5. Nine Goddesses are Hot for the Military
While writing my “Korean Sociological Image #72: Girl-group performances for the military” last summer, it proved surprisingly difficult to find actual embeddable videos of those. So, via Omona They Didn’t!, here are 3 with Nine Muses from earlier this year, who seem to be quite popular with the troops:
 6. Premarital pregnancy gets trendy
6. Premarital pregnancy gets trendy
My 2008 post, Why Korean Girls Don’t Say No: Contraception Commercials, Condom Use, and Double Standards in South Korea, is still my most popular and most-commented, despite being based on 2003 data, and displaying what were then big, obvious gaps in my knowledge of Korean sexual mores. Hopefully I’ve filled most of those since, not least because one commenter pointed out that Koreans have always been quite tolerant of premarital pregnancies, so long as the couple planned to marry.
What’s more, according to the Korea Times, now they’re more common than ever. Some excerpts (source, above-right):
Celebrity couples such as actor Jang Dong-gun and his wife Ko So-young, and Kim Seung-woo and Kim Nam-joo, have admitted they walked down the aisle with the brides pregnant.
Actress Kim Bu-sun goes as far as to say she approves of premarital pregnancy.
“My premarital pregnancy was the best thing that ever happened to me,” Kim says. “If my daughter becomes pregnant, I will host a party in her honor.”
She believes people should embrace single mothers, whom she considers a minority in need of attention and care.
Nice to hear, considering the Ministry of Health and Welfare defined unwed mothers as “ignorant whores” as recently as 2010 (technically, it was “low levels of education [and] impulsive sexual drives”). Continuing:
But premarital pregnancy is now humdrum, even among people who are not stars.
In a survey that consultancy Duo Wed conducted between June 1 and June 14, one-third of 374 newlyweds questioned said the bride was pregnant when they married.
Of these couples, 92.1 percent said their babies were unexpected.
Read the link for the rest. Note that this doesn’t mean Koreans are necessarily becoming more tolerant of cohabiting couples however (and who face a lack of suitable accommodation anyway), nor of pregnancies that don’t lead to marriage.
7. This Dude’s Response To Female Crotch Sweat Shame Is Perfect
See Bust for more. Fortunately, I haven’t seem any similar products advertised here yet, and perhaps that’s because there will never be a market for them, as Korean women generally don’t sweat as much as those of other races. This was discussed in my 2010 “Hot Sweaty Korean Women” post, about a rare Korean commercial that did feature a Korean woman sweating:
Please note I also made some overgeneralizations about Korean (women’s) exercise and gym culture in that post though, and would write it very differently today. But on the plus side, readers soon corrected my mistakes, and it (hopefully) remains useful for the journal study on Korean attitudes to dieting it references.
Also, for a related 2009 post on why Koreans generally don’t wear deodorant, its marketing, and the implications for Korea’s kkotminam (“pretty flower men”), which I recently updated and does still hold up today, please see “The Scent of a Man: What deodorant commercials tell us about Korean metrosexuality.”
Thoughts? On any of stories above?
Quick Hit: Korean police blaming sex crimes on scantily clad women
 (Sources: left, right)
(Sources: left, right)
From the Korea Times:
The government is vowing stronger punishment on sex offenses. As a start, the Justice Ministry has rewritten the law to allow law enforcement authorities to investigate and prosecute sex criminals without a complaint filed from the victim.
But were loose laws ever much of a problem because the majority of our obtuse police officers are regressive enough to claim that some female victims simply had it coming?
The Korea Women’s Development Institute recently quizzed some 200 police officers in South Gyeongsang Province cities over their thoughts on sex crimes against women and the results were disturbing.
About 54 percent of the respondents supported the view that women who wear revealing clothing are somehow culpable in any attacks on them. Around 37 percent of them felt the same about women who drink and 21 percent about women walking alone at night. And 24 percent said they found it difficult to believe a victim when they don’t report the incident right away.
Read the rest at the link. Meanwhile, I’ll try to find the original KWDI report on the survey and/or related news article, and translate it for you by sometime next week.
Also, for anyone interested in the Korean Slutwalk (잡년행진), see here for information about the last two years’ events. I’ve been unable to find any information about this year’s, but do hope that one will go ahead. After all, as the police officers’ attitudes above indicate, unfortunately it’s needed more than ever…
Update: I’m No Picasso has a must-read response to the article.
Raising the Dead: The Future of Advertising?
 (Sources: left{edited}, right)
(Sources: left{edited}, right)
Via Phenomenology/Intervention:
CGI technology has brought the late Audrey Hepburn back to the screen, as she stars in a TV advertisement for the chocolate company, Galaxy. Hepburn’s sons, Sean Ferrer and Luca Dotti, said regarding the project: “Our mother often spoke about her love of chocolate and how it lifted her spirit, so we’re sure she would have been proud of her role as the face of Galaxy.”
It made the author a little queasy, and reminded her(?) of “Pat Metheny’s rant on ‘musical necrophilia,’” which is “the technique of overdubbing on the preexisting tracks of already dead performers.” For those more interested in the likely impact on entertainment and politics as the technology becomes more widely available though, I recommend the 2008 short story “Fenneman’s Mouth” available at the science-fiction podcast Escape Pod, which explores the making of a new Groucho Marx (1890-1977) movie, and then the rewriting of a senator’s comment on television.
 Commenter k23 said of it (source, right):
Commenter k23 said of it (source, right):
While not too big on the action, it did get me thinking about the plausibility of the story. While I understand the concept of manufactured memories, I think that if we were aware of the technology that could alter videos to that advanced degree, it will spawn a contingent that will publicly question, research, and often discredit every video that is produced. It’s happening right now with still photographically, like when the blogosphere was quick to research and discredit Iran’s missile launch photos.
And DaveNJ:
I love this story from a sci-fi and personal perspective….You’ve got a story where a group of people create a new piece of technology and use it originally for entertainment purposes, but during the course of the story the technology changes the face of politics as we know it…
Against that, Meercat commented that the technology was already very much in use:
Granted, we are led to believe the characters have improved the technology to the point that it appears real, but current real-life animation, sophisticated voice over, etc. does the same thing. These things have been used for several years to sell products, complete films and I would guess even fabricate more than a few factual accounts. A couple of years ago, a product, Coca-cola I think, had a series of advertisements featuring Bing Crosby and other dead celebrities. It was pretty rough, but the concept and execution is there.
Indeed, it is in this sense that one of the first links to this part of the world emerges. For according to Joe Joseph in The Japanese: Strange But Not Strangers (1993), print advertisements of dead celebrities were used there for many decades (pp.112-3; source, right):
 Japan first began hoovering up American film stars in the 1950s, a golden age when America stood for baseball, hamburgers, Hollywood, and everything else that a still poor Japan yearned for. Some of the starts from that golden age are still winking from commercials and hoardings across Japan, even though they died years ago. Irritatingly for the estates of these actors, Japanese law does not oblige Japanese firms to pay royalties for ‘portrait rights’ of dead stars. So James Dean promotes just about everything in Japan from hygienic rubber gloves to high-tech robots. He is infinitely obliging. You only have to ask and he will personally endorse your noodle restaurant or petrol station. Marilyn Monroe’s face also peers out of the unlikeliest posters in the unlikeliest places.
Japan first began hoovering up American film stars in the 1950s, a golden age when America stood for baseball, hamburgers, Hollywood, and everything else that a still poor Japan yearned for. Some of the starts from that golden age are still winking from commercials and hoardings across Japan, even though they died years ago. Irritatingly for the estates of these actors, Japanese law does not oblige Japanese firms to pay royalties for ‘portrait rights’ of dead stars. So James Dean promotes just about everything in Japan from hygienic rubber gloves to high-tech robots. He is infinitely obliging. You only have to ask and he will personally endorse your noodle restaurant or petrol station. Marilyn Monroe’s face also peers out of the unlikeliest posters in the unlikeliest places.
I would be grateful if any readers can tell me if that is still the case, and/or whether they were also used in Korea (I haven’t seen any in the last thirteen years here). Either way, the second link emerges in that given that Korea is a society not just lagging in implementing legislation on advertisers disclosing the use of Photoshop, but arguably one that positively embraces its use, then I fully expect Koreans to be at the forefront of using such technology in the future.
And soon. Recall how quick and easy it already is to do extensive digital manipulation of video — not just images — these days, as demonstrated in the following video (hat tip to maitretya). It takes no great leap to see how dead celebrities could be used instead of living actors:
And that video was from 2010, just after a similar technology was used for a Georgia coffee commercial (see here for a discussion and more examples):
The money shot:
 (Sources: left, right)
(Sources: left, right)
But while there is definite cause for concern, especially given that the Korean media and advertisers already present physically-impossible, computer-generated body shapes for consumers to aspire to, I shouldn’t deny that there are also benefits to photo and video-manipulation, or that retouching has existed just as long as both technologies themselves. These considerations are well covered in the following short Off Book video (which in turn is further discussed at PetaPixel):
Accordingly, I’m more fascinated than left queasy by the Audrey Hepburn commercial, and particularly enthused by the similarities to an SF story I read just five years ago. For those of you similarly inspired by such a connection, I highly recommend Sociology Through Science Fiction (1974), edited by John Milsted and Martin Greenberg, for further reading if you can ever get a hold of a copy (see a review here), or “Expanding the Sociological Imagination: Teaching Sociology with Speculative Fiction” at The Sociological Cinema for something (much) more recent and accessible.
 (Source)
(Source)
Thoughts? Any more examples, or suggestions for further reading?
Update: John from Daejeon provides some great — and really quite old — examples here. In hindsight, the Galaxy commercial only stands out for its technological sophistication, not its concept.
Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 5: Links
 (Source: Vivien)
(Source: Vivien)
In Part 4 back in February, I mentioned that Korean women were getting less breast augmentation and more breast reduction procedures than their counterparts in the US and Brazil, despite having a genetic predisposition towards small(er) breasts. Add that North Koreans think busty women are “intentionally and lewdly stressing [their] femininity,” and that Wacoal’s ‘Bra That Makes Big Breasts Look Small’ would probably be just as popular in Korea as in Japan, then I wrote that all signs point to “a big disconnect between ordinary Koreans’ — and even models’ — attitudes to fashion, body image, and sexuality and what you may see on Korean TV.”
 As Dr. Roald Maliangkay at the Australian National University points out however, it’s very much the same with men:
As Dr. Roald Maliangkay at the Australian National University points out however, it’s very much the same with men:
….The majority of men appearing on posters and billboards are celebrities. Although the wide use of cosmetic surgery is making men look increasingly similar, they are often associated not merely with a product, but also with a popular drama, and in some cases, a steamy bed or bathroom scene. That is not something the average worker would ever seek to emulate, nor be able to, as the nation’s corporate dress code remains conservative.
See “The bra boys of South Korea” at World News Australia for more, which is mostly about the kkotminam (꽃미남) phenomenon, or here for more on the disproportionate role of celebrity endorsements in the Korean media (source, right: Wonbin Thailand).
Next, in Part 4 I also discussed how official North Korean attitudes to women’s clothing have been changing in response to women increasingly becoming breadwinners, generally becoming more restrictive. For more on this “Female Face of North Korean Capitalism,” see Andrei Lankov’s recent lecture at the Royal Asiatic Society in Seoul:
Third, via Lisa Wade at Sociological Images, here is:
…a great short clip instructing women workers newly employed in industrial factories during World War II on how to do their hair to maximize safety. It assumes both ignorance and vanity on the part of women and speaks to the lack of efficiency caused by efforts to remain attractive on the line.
As I pointed out in — yes, again — Part 4, those assumptions about vanity need to be placed in the context of wartime shortages, when attention to beauty and fashion were viewed as extravagant and unpatriotic. But despite that, women’s anxieties about both were still explicitly encouraged, preyed upon, and/or encouraged by industry, and actually even by the government itself. The ensuing contradictions, double-standards, hypocrisy, and backlash are very similar to what has been occurring in South Korea since the 2000s with women’s rapid entrance into the (part-time) workforce, and make comparisons very useful and compelling.
 For more on the backlash in Korea specifically, see “The hate underlying the ‘__ Girl series’ and criticism of women’s organizations” at ILDA (in addition to all the links in previous posts in the series). Finally, for more on the wartime US case, first see “The Impact of War on 1940′s Fashion in the USA” at Glamor Daze for a primer on women’s fashions in the period; then, see Bored Panda for rare color photographs of women working in aircraft manufacturing plants in World War Two, taken by:
For more on the backlash in Korea specifically, see “The hate underlying the ‘__ Girl series’ and criticism of women’s organizations” at ILDA (in addition to all the links in previous posts in the series). Finally, for more on the wartime US case, first see “The Impact of War on 1940′s Fashion in the USA” at Glamor Daze for a primer on women’s fashions in the period; then, see Bored Panda for rare color photographs of women working in aircraft manufacturing plants in World War Two, taken by:
“Alfred T. Palmer who worked for the Office of War Information (responsible for promoting patriotism, war news management and women recruitment)” whose photos “had to lure young women into the factories by showing women workers as glamorous and even fashionable.” (My emphasis; see example on right).
Update: also see Kathryn M. Brown’s 2010 MA thesis Patriotic Support: The Girdle Pin-up of World War 2 (it can’t be directly linked sorry—type the title into the searchbar) for more on how malleable and adaptable — and, as explained, ultimately hypocritical and contradictory — the language, prevailing standards for, and attitudes towards beauty and fashion proved to be for the needs of government and industry (see Part 3 for modern Korean and earlier US parallels also).
The Revealing the Korean Body Politic Series:
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic Part 12: If You Don’t Have Kim Yuna’s Vital Statistics, Your Body Sucks and You Will Totally Die Alone
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 11: 노출이 강간 유혹?…허튼소리 말라 Wearing Revealing Clothes Leads to Rape? Don’t Be Absurd
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 10: “An epic battle between feminism and deep-seated misogyny is under way in South Korea”
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 9: To Understand Modern Korean Misogyny, Look to the Modern Girls of the 1930s
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 8: The Bare-leg Bars of 1942
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 7: Keeping abreast of Korean bodylines
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 6: What is the REAL reason for the backlash?
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 5: Links
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 4: Girls are different from boys
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 3: Historical precedents for Korea’s modern beauty myth
- Revealing the Korean Body Politic, Part 2: Kwak Hyun-hwa (곽현화), Pin-up Grrrls, and The Banality of Sex and Nudity in the Media
- Bikinis, Breasts, and Backlash: Revealing the Korean Body Politic in 2012
Reader Requests and Upcoming V-Day Events
 (This Must be the Place, Roy Lichtenstein, 1965. Source)
(This Must be the Place, Roy Lichtenstein, 1965. Source)
— First, the next 2 weekends are just jam-packed with V-day related events, culminating in the Vagina Monologues performances. See Busan Haps for those happening in Busan, and KoreaMaria for Gwangju.And if anyone knows of any more events being held in different cities, please let me know!
— Next, a request from Arianna Casarini (almostelse@gmail.com), who is looking for Korean or East Asian artists that reflect on cosmetic surgery and/or body-image. Unfortunately, I don’t know of any myself, so (with permission) I’m reprinting her email here:
I’m an Italian student of the University of Bologna, close to get my first degree.
Very little after I started getting deeper in the study of Korean culture, I discovered your blog and your illuminating articles, and thanks to it I became especially interested in the problem of the pervasiveness of cosmetic surgery in the South Korean reality.
Since I found the subject really deep and stimulating, I decided to make it the subject of my graduation thesis.
In my thesis, I want to focus on the connection between Art (especially Contemporary Art) and cosmetic surgery, both in Eastern and Western countries. I wish to focus on inspecting the interpretations and criticisms that Contemporary Art gives on the problem of cosmetic surgery, and on the mutual influence that Art and aesthetic plastic surgery have on each other, paying attention to all the psychological and sociological matters implied.
Even though I’m quite well informed on the side of contemporary Western artists whose artworks dwell on cosmetic surgery, I lack a deep knowledge of East Asian artists and I wondered if you could help me on this matter.
Could you indicate me Korean/East Asian artists that reflect on cosmetic surgery/body problems or some essay that treats this subjects?
Sadly I can’t read Korean, so I must specifically look for English sources.
I’m really glad I found your blog and that, thanks to it, I have been able to get to know your interesting work.
I thank you in advance for your attention,
— Finally, Ashley Turner is looking looking for people with experience in web design, visual/graphic arts and audio/video editing who may interested in assisting with a Hallyu project:
Our vision is to help bridge the cultural gap between America (and other Western countries) and Korea by bringing all enthusiasts of Korean culture in a social project that encourages cultural exchange between all fans; as well as making conversation about it accessible to everyone by integrating and welcoming international fans. It is about proving the power of cultural exchange to balance the connection between Korean and international fans and bringing culture outside the context of K-pop, as well as using K-pop as gateway to the rest of culture. The project will serve as a casual learning entry point that makes the Hallyu wave accessible, and allows people reflect on their own culture in relation to Korea’s….
….This project is a social media website being funded by the Korean Cultural Center Washington D.C. and KOFICE (Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange).
The corresponding proposal [ask Ashley for a copy] has further information concerning the individual aspects of the project. Those with experience in web design, graphic arts, and audio/video editing are being actively scouted. This is primarily a volunteer opportunity with potential for compensation later in development. If you are interested in participating, please contact Ashley at ashley.trnr@gmail.com.
Any readers who also have requests and/or would like events publicized, please just email me and I’d be happy to post them on the blog (and apologies for the slight delays with these ones). To make it easier for me though, when you do please just send something I can quickly copy and paste. Thanks!




