“It was there for literally 0.1 seconds! And drawn by a guy! And…and…WHY THE HELL DO YOU FEEL SO THREATENED BY IT ANYWAY??”
 Estimated reading time: 12 minutes. Photo by Timur Weber @Pexels.
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes. Photo by Timur Weber @Pexels.
It’s always heartwarming when a columnist literally calls bullshit on the Korean manosphere.
For that sass alone, in a moment I’ll gladly pass on to you my full translation of Hankyoreh Gender Team Leader Jang Su-gyeong’s accusation, written in December 2023 about the MapleStory controversy of the previous month.
But for all her flair, I think it was a little misdirected.
 “I am very interested and concerned about hatred and discrimination, which hang as prevalent and thick in Korean society as air.”
“I am very interested and concerned about hatred and discrimination, which hang as prevalent and thick in Korean society as air.”
Basically, she criticizes the controversy for being only the latest example of the ‘feminist check’ tactic the Korean manosphere engages in these days. Whereby they: go bananas over any alleged instance of a small penis finger gesture; dig deep to find evidence that those responsible have even the slightest of feminist leanings; then shrilly demand the company responsible fire them and remove the offending gesture.
This is more pernicious and impactful than it may sound to outside observers. Emboldened by the term “feminism/페미니즘/女性主義” more accurately meaning radical feminism in Korean, to most men and women alike, virtually anyone even only indirectly advocating for sexual equality can get tarred with that brush. And when that happens, say, for wearing t-shirts incels don’t like, companies are only too eager to throw those real or alleged “femis/페미” under the bus, all for the sake of appeasing the manosphere.
 Source: John Marcotte.
Source: John Marcotte.
So I share her ire, and don’t want to get too hung up on semantics. It’s just that, precisely because the manosphere can be so loud and proud about what they doing, why they’re doing it, and who they’re hurting, with absolutely no subterfuge necessary, perhaps “bullshitting” isn’t the best way to describe the process.
Or, perhaps I only say that with the benefit of hindsight.
Because as if to prove her point, an even more bullshit controversy, over nonexistent government plans to switch the genders of emergency exit signs, is emerging as I type this a month later.
As you’ll see after her column, it’s a much more blatant example of what she describes. Especially when you contrast it with a real example, which there was a clear need for, made nationwide to the caregiver figures in subway escalator signs in the late-2000s. And which, to the best of my knowledge, did not result in any harm to anyone’s sense of manhood—no matter how deeply the Korean manosphere seems to feel threatened if the same ‘concessions’ were made today.
 Left: the offending gesture, which is visible for precisely 0.1 second. Full screenshot source: 원정상 @YouTube. (For the record, I just thought it was too good a screenshot not to steal—I don’t know the YouTuber’s stance on the controversy.)
Left: the offending gesture, which is visible for precisely 0.1 second. Full screenshot source: 원정상 @YouTube. (For the record, I just thought it was too good a screenshot not to steal—I don’t know the YouTuber’s stance on the controversy.)
너 페미니? Are You a Femi?
장수경/Jang Su-gyeong, 2023-12-17 (flying710@hani.co.kr/@jsggija)
“너는 페미니스트야?”
“Are you a feminist?”
몇달 전 대학 때 친하게 지낸 남자 동기를 만나 들은 질문이다. 질문을 받은 뒤 처음 느낀 감정은 당황스러움이었다. 그동안 받아본 적 없는 질문이었기 때문이다. 페미니스트냐 아니냐를 따지는 게 무의미할 정도로, 나는 스스로 페미니스트가 아니라는 생각을 해본 적이 없던 터였다.
This is a question I was asked a few months ago, when I met a male classmate with whom I was close to in university. My first reaction was embarrassment. Because it was a question I’d never been asked before. I’d never thought of myself as *not* a feminist, to the point where it was meaningless to consider whether I was one or not.
“나는 페미니스트지.”
“Yea, I am a feminist.”
“왜 너 자신을 그렇게 규정해? 네가 생각하는 페미니즘이 뭐야?”
“Why do you define yourself like that? What do you think feminism is?”
“여성과 남성은 동등하고, 성별에서 오는 각종 차별을 없애야 한다는 거지.”
“I think it means women and men are equal, and so all kinds of sexual discrimination must be eliminated.”
“그건 인권 차원에서 당연한 거 아니야?”
“Isn’t that only natural from just from a human rights perspective though [So a feminist one isn’t necessary]?”
친구는 페미니즘의 방향에는 동의하면서도 페미니스트에 대해서는 부정적 생각을 가진 듯했다. 친구는 내게 “너의 정체성을 어느 하나로 규정하지 않길 바란다” “역차별당하고 있다고 주장하는 2030 남성들의 이야기도 귀담아들어달라”는 말을 남겼다.
Although my friend agreed with the general direction of feminism, he seemed to harbor negative thoughts about feminists themselves. He continued, “I hope you don’t define your identity as just this one thing,” and “Please listen to the stories of men in their 20s and 30s who claim they are being reverse discriminated.”
최근 게임 업계에서 일하는 여성 작가들을 향해 잇따르고 있는 ‘페미니즘 사상 검증’ 사태를 지켜보면서 당시 대화를 떠올린 건, 페미니스트를 옥죄는 사회 분위기가 전방위적이라는 생각 때문이었다. 친구의 질문 의도가 ‘사상 검증’일 것이라곤 생각하지 않는다. 다만, 이런 질문이 나와 동등한 위치에 선 사람의 ‘순수한 궁금증’에서 비롯된 것이 아니라 누군가를 검열하고, 억누르고, 일자리를 겨냥하고 있다면 말은 달라진다.
While watching the recent ‘feminist check’ [lit., ‘verification of feminist ideology’] that has been taking place against female writers working in the game industry, I remembered the conversation at that time because I thought that the social atmosphere that oppresses feminists is omnipresent. I don’t think the intention of my friend’s question [was malicious], to confirm that I was a feminist [and then target me on that basis]. However, if these questions do not arise from a place of genuine curiosity [and willingness to engage in dialogue] expressed by a person standing on equal footing with me, but instead is a form of sealioning aimed at censoring, suppressing, or targeting someone’s job, the story is different.
지난달 말 남초 사이트와 게임 업체 넥슨이 한 행동은 전형적인 ‘사상 검증’이었다. 남초 커뮤니티는 넥슨의 게임 ‘메이플스토리’ 홍보 영상에 등장하는 캐릭터의 손가락 모양을 두고 ‘남성 혐오’라고 주장했다. 근거는 빈약했다. 해당 영상을 작업한 하청 업체의 한 여성 직원이 자신의 사회관계망서비스 계정에 올린 페미니즘 옹호 발언이 전부였다. 전형적인 확증 편향이었지만 넥슨은 별다른 사실관계 확인 없이 해당 영상을 비공개하고 업체 쪽에 법적 대응을 예고했다.
At the end of last month, the actions taken by the manosphere sites and forums, and then the game company Nexon’s responses, were a typical example of the feminist check process. The manosphere claimed that the shape of the finger of the character appearing in the promotional video for Nexon’s game *MapleStory* was ‘man-hating.’ But the evidence was actually quite weak. A female employee of the subcontractor who worked on the video uploaded it to her social networking service account, and all she said was her defense of feminism. It was a typical confirmation bias, but Nexon made the video private without verifying the facts and announced legal action against the subcontractor she worked for?
이후 해당 작업물을 그린 이는 40대 남성 애니메이터라는 사실이 보도됐다. 주장의 근거가 사라졌으니, 남초 커뮤니티가 사과했을까. 아니다. 애초 사실 여부는 중요하지 않다는 듯, ‘언론의 보도가 거짓’이라거나 ‘남페미는 문제가 아니냐’며 방향을 틀었다. 그사이 해당 여성 직원은 개인 신상 정보가 털리고 온갖 욕설을 듣는 등 사이버불링을 당했다.
However, it was later reported that the person who drew the work was actually a male animator in his 40s. Now that the basis for the claim has disappeared, did the manosphere apologize? Not at all. In the first place, it seemed as if it didn’t matter whether it was true or not. And then they changed direction by saying, “The media’s reports were false,” or “Aren’t male feminists the real problem here?” Meanwhile, the female employee suffered cyberbullying, including having her personal information stolen and receiving all kinds of abusive language.
퓰리처상을 받은 영국의 저널리스트 제임스 볼은 책 ‘개소리는 어떻게 세상을 정복했는가’에서 ‘진실이든 거짓이든 신경 쓰지 않는 사람들이 만들어내는 그럴싸한 허구의 담론’을 ‘개소리’(bullshit)라고 말했다. 개소리꾼의 개소리는 거짓말과 달리 자신이 원하는 결과를 얻기 위해 최소한의 진실조차 중요하지 않기에 거짓말보다 해롭고, 팩트로 대응해도 힘을 잃지 않는다고 했다.
In his book Post-Truth: How Bullshit Conquered the World (2021), Pulitzer Prize-winning British journalist James Ball said that ‘bullshit’ is “a specious fictional discourse created by people who do not care whether it is true or false.” He said that unlike lies, this, the most bullshit of bullshits, is more harmful than lies because even the minimum amount of truth is not important to achieve the results one wants, and it does not lose its power even if it is responded to with facts.
“업장에서 왜 사회운동을 하냐”(허은아 국민의힘 의원), “악질적인 점은 실수가 아니라 의도적이라는 데 있다”(이상헌 더불어민주당 의원), “의도를 가지고 넣었다면 조롱”(류호정 정의당 의원)이라는 정치인들의 반응은 ‘개소리’ 기세를 더 강화할 뿐이었다. 정치권의 메시지는 ‘사상 검증을 하지 말라’ ‘페미니스트가 뭐가 문제냐’여야 했다. 기업은 개소리꾼의 개소리를 수용할 것이 아니라 무시해야 했다. 언론은 ‘집게손 논란’이라는 제목으로 개소리를 앞다퉈 보도하지 말아야 했다.
The politicians’ responses—“Why are you engaging in social movements at your workplace?” (People Power Party Rep. Heo Eun-ah), “The malicious point is not that it was a mistake, but that it was intentional” (Democratic Party Rep. Lee Sang-heon), “If it was put in with intention, it would be ridiculed” (Justice Party Rep. Ryu Ho-jeong)—only added to the bullshit’s momentum. Instead, the message from the political world should have been, “Don’t engage in a feminist check,” and “What’s the problem with feminists anyway?” Companies should have ignored this bullshit of bullshits, not blindly accepted it, and the media should not have rushed to report it under the title ‘Claw Hand Controversy.’
‘페미니스트는 남성 혐오론자이기 때문에 그런 집게손가락 모양을 넣었을 것’이라는 ‘개소리 담론’에 기업, 정치인, 언론 등이 동조한 결과는 ‘일터를 잃는 노동자’다. 2016년 ‘소녀에게 왕자는 필요 없다’는 글이 쓰인 티셔츠를 입었다는 이유로 교체된 성우처럼, 과거 에스엔에스에 페미니즘 관련 글을 올렸다는 이유로 2023년에 계약 해지된 게임 ‘림버스 컴퍼니’의 그림작가처럼 말이다.
 Source: Twitter/@KNKNOKU via BBC.
Source: Twitter/@KNKNOKU via BBC.
The result of companies, politicians, media, and so on agreeing with the bullshit discourse, that “feminists must have put that index finger symbol because they are male haters,” is workers losing their jobs. Just like the voice actor who was replaced in 2016 for wearing a T-shirt with the words “Girls do not need a prince” written on it, the illustrator of the game Limbus Company whose contract was terminated in 2023 for [retweeting tweets that used derogatory terms for men].
개소리를 하며 ‘사상 검증’을 정당화하는 이들에게 말해주자. 너희 주장은 개소리라고. 페미니즘이 뭐가 문제냐고. 너희들이 페미니즘을 알긴 아느냐고.
Let’s tell those who spew bullshit in the name of feminist checks: Your arguments are bullshit. What’s the problem with feminism anyway? Do you guys even know *anything* about feminism? (END)
(For more information, in chronological order over November to December, including the response of the Nexon Union, please see the Korea JoongAng Daily, this Reddit thread, Korea Bizwire, the Korea Times, and again the Korea JoongAng Daily.)

Now fast forward to mid-January 2024, when multiple media outlets reported that in the name of gender equality, the government was immediately replacing the ‘male’ pictogram in some of the emergency exit signs nationwide with more obviously ‘female’ ones. Some outlets added that it was at the behest of women’s groups.
I’m sure I don’t need to outline the absurdities of such a plan. Nor that (most of) the multiple, eminently justifiable criticisms, did not necessarily stem from misogyny.
But more often than not, feminists became the target anyway.
Because at best, the new design was actually just one of many possibilities considered for updating the signs, to replace the existing ones only as per needed (so, no extra cost at all). Whereas at worst—and it’s unclear which applies, frankly—it was a complete fabrication of the media.
As were the supposed women’s groups that were demanding it:
직장인 A씨(29)는 “새 픽토그램을 보니 긴 머리에 치마를 입고 가슴 부분이 튀어나와 있었다”며 “여성 중에 이런 기호를 원하는 사람이 실제로 얼마나 되겠냐. 오히려 여성을 희화화한 듯하다”라고 말했다. 한 누리꾼은 “누군가 일부러 논란을 만들었다고 생각될 정도”라고 했다.
한 여성단체 관계자는 “어떤 기사에선 ‘여성단체 등이 요구해왔기 때문’이란 식으로 설명했던데, 그런 요구를 한 단체가 어디에 있나. 괴담 수준의 터무니없는 얘기”라며 “오히려 성 고정관념을 고착화하는 그림이다”라고 비판했다. (Kyunghyang Shinmun)
Office worker A (29) said, “When I looked at the new pictogram, I saw her with long hair and a skirt and her breasts sticking out,” adding, “How many women actually want this symbol? “In fact, it seems like a caricature of women.” One netizen said, “It almost makes you think someone created controversy on purpose.”
An official from a women’s group said, “In some articles, it was explained as ‘because women’s groups have been making demands,’ but where is the group that made such demands?” “It is an absurd story at the level of a ghost story,” he criticized, adding, “Rather, it is a picture that perpetuates gender stereotypes.”
And from the Dailian:
…”이런 것도 성별 갈라치기 소재로 쓰냐” 라는 등 비판 의견이 쏟아졌다.
…[Netizens] said “Is this just another thing that can be used to divide the sexes?”
 Image sources: 스포츠하국, Pixabay (edited).
Image sources: 스포츠하국, Pixabay (edited).
Now, you could rightfully argue that the media was responsible in that case, not technically the manosphere.
Only, there’s a great deal of synergy between the two.
Crucial context is that the notoriously clickbaity Korean media is one of the least trusted in the (developed) world, and that it is heavily male-dominated. Add that Korea is a deeply patriarchal country, currently in the midst of a polarizing “gender war,” then a constant backlash of ‘journalists’ scapegoating feminists for all Korea’s ills is all too predictable.
The deceit involved can be staggeringly blatant and obvious. I’ve even caught out with one bullshit story myself. When, after ‘reporting’ on a literally non-existent controversy over Berry Good member Johyun‘s cosplay above, then getting the sought-after inflamed response from the manosphere, the media added insult to injury by blaming the entire controversy on the reports of a single female reporter, who criticized Johyun for her overexposure despite praising male nudity in previous articles.
Only, her article on Johyun wasn’t published until several hours after news about about the controversy first appeared. (And ironically, her article wasn’t at all like it was described; in fact, they it was just as clickbaity as everyone else’s, and provided no basis to label her a feminist.)

 Sources: MLBPark (1; since deleted); 2)
Sources: MLBPark (1; since deleted); 2)
But still: these three cases alone are insufficient evidence of systematic misogyny by Korean journalists and the media. I do strongly suspect though, that a thorough investigation by academics, media-watchdogs, and/or feminist groups will undoubtedly reveal that such an agenda exists. Likely, many such investigations have already been conducted, so I’ll follow this post up with those at a later date.
In the meantime, Korean or otherwise, I will never, ever trust any news source that makes claims about unnamed women’s and feminist groups.
As part of my own 2024 agenda though, I try to highlight the positive where I can, and can’t end on that note.
So, with my apologies for the crappy quality of my digital camera back in the late-2000s, finally let me remind you of when, in a bid to challenge antiquated gender roles and encourage more equitable childcare between parents, subway-caregiver signs with a female figure were gradually replaced with an androgynous one. They were only replaced as per needed, so they didn’t cost extra money, leaving even the most vitriolic of incels struggling to oppose them without exposing their misogyny. Which is probably why I haven’t actually seen one with a female caregiver ever since.
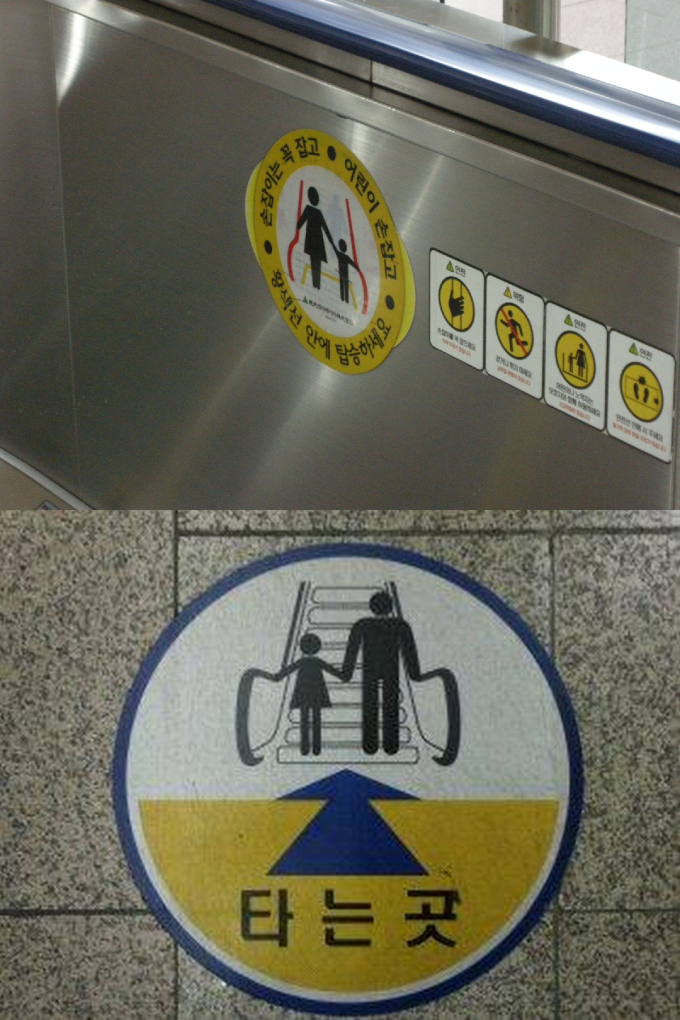

Only, doing my due diligence, I’m sorry to report that today I learned my experience isn’t at all universal (let alone my nonexistent experience of female spaces). That the initiative stalled, and that as of 2019, many Seoul subway stations still have almost entirely female caregivers in their signs. Most ironically and symbolically perhaps, in Gangnam Station, where 100% of them are of women:
 Source: Hankook Ilbo.
Source: Hankook Ilbo.
So, the fight continues, even over the little things. But it does continue.
Related Posts:
- The Korean Conscription System Promotes a Servile, Subordinate, Sexually-Objectifying View of Women. Here’s How.
- “Sex, Sass, and Sensibility in South Korea” 뭐야?
- “An epic battle between feminism and deep-seated misogyny is under way in South Korea”
- The Hidden Roots of Korea’s Gender Wars
- There are More Entry-level Korean Women Journalists than Men These Days. So Why do Most Leave the Industry in Less Than 10 Years?
- Manufacturing Outrage Against Feminists: The Cosplay Edition
If you reside in South Korea, you can donate via wire transfer: Turnbull James Edward (Kookmin Bank/국민은행, 563401-01-214324)














 The Quora commenter who posted that continued:
The Quora commenter who posted that continued: Because today I learned that in addition to all the other, more obvious barriers and hurdles that discourage girls and women, that this extends to them even displaying the necessary character traits to succeed too. That it’s not that they don’t also want to geek out over the things only boys are “supposed” to like, necessarily. Just that if they do, they’re much more likely to be criticized for their obsessiveness. Whereas among boys and men, that same obsessiveness tends to be seen as a virtue instead.
Because today I learned that in addition to all the other, more obvious barriers and hurdles that discourage girls and women, that this extends to them even displaying the necessary character traits to succeed too. That it’s not that they don’t also want to geek out over the things only boys are “supposed” to like, necessarily. Just that if they do, they’re much more likely to be criticized for their obsessiveness. Whereas among boys and men, that same obsessiveness tends to be seen as a virtue instead. Still wanting to flex how smart I am though (did I mention I’m single?), I want to causally convey how there must surely be a reason why chess is still considered a symbol of high intelligence, even genius too, at least in the West (I concede that
Still wanting to flex how smart I am though (did I mention I’m single?), I want to causally convey how there must surely be a reason why chess is still considered a symbol of high intelligence, even genius too, at least in the West (I concede that 

















































 Screenshots from
Screenshots from 





























